The stainless steel protractor with two arms, size 90x300mm, allows the user to draw at a fixed angle. This compact and lightweight stainless steel protractor is widely used in engineering, angle measurement, student drafting, architectural design, woodworking, length measurement, etc.

High quality stainless steel angle protractor, robust and durable
- 90x300mm Stainless steel angle protractors are highly accurate and precise in measuring angles, ensuring that your measurements are as close to perfect as possible.
- The 180-degree angle finder ruler has a laser scale for accurate and practical reading.
- The two arm stainless steel construction of angle protractors makes them very durable and resistant to wear and tear, ensuring they can withstand frequent use and last for a long time.
- SISCO two arm stainless steel angle protractor is lightweight and compact, making them easy to carry around and use on the go.
Application
Angle protractors are commonly used in fields such as construction, engineering, and carpentry to measure angles for cutting and fitting materials. They are also used in mathematics and physics to solve problems involving angles and trigonometry.
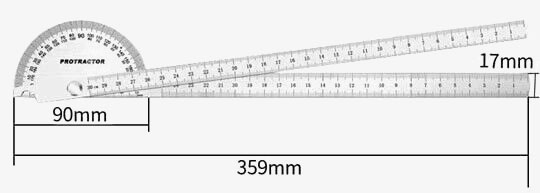
- Model: SISCO-AP-TA90150
- Measuring Range: 0-180 degrees
- Size: 90x150mm
- Total Body Length: 197mm
- Diameter of Disc: 90mm
- Width: 14mm
- Body Thickness: 1.2mm
- Weight: 95g
Dimension (Unit: mm)
Q1: What is an angle protractor?
A1: An angle protractor is a measuring tool used to measure angles. It typically consists of a flat, plastic or metal base with a pivoting arm that has a graduated scale marked in degrees. The arm can be rotated to any angle, allowing the user to measure the angle between two lines or the angle of a single line relative to a horizontal or vertical axis.
Q2: How do I use an angle protractor?
A2: To use an angle protractor, place the base of the protractor on the surface you wish to measure the angle of. Align the protractor's vertical or horizontal axis with one of the lines you want to measure the angle between. Then, rotate the protractor's arm until it is aligned with the other line you want to measure. Read the angle measurement from the graduated scale on the arm.
Q3: What are some common applications of angle protractors?
A3: Angle protractors are commonly used in a variety of applications, including carpentry, metalworking, engineering, and drafting. They are often used to measure the angle of a cut to ensure it is accurate and to create angled cuts for various projects. They are also useful in determining the slope of a roof or the angle of a hillside. In addition, angle protractors can be used in mathematical and scientific applications to measure angles between lines or to calculate trigonometric functions.
Tips: What are the measurements of a protractor?
A protractor is a measuring tool used to measure angles. The measurements on a protractor are typically marked in degrees and are divided into 360 degrees. The protractor is usually a semi-circular or circular tool with a base marked with numbers from 0 to 180 degrees in a clockwise direction, and sometimes also marked in a counterclockwise direction. The degrees are further divided into smaller units, such as minutes (') and seconds (").
The markings on a protractor can vary slightly depending on the specific type and brand, but some common features of a protractor include:
- A straight edge or base line helps to align the protractor with the angle being measured.
- A center point, sometimes marked with a small hole, is used as a reference point for measuring angles.
- Two sets of numbers or markings, one on each side of the center point, indicate the degrees and smaller units of measurement for the angle being measured.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

