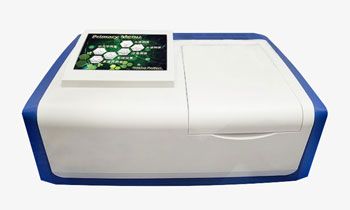
UV Visible spectrophotometers adopt split beam optical system, with large internal memory capacity, which can store test results, scanning images, regression equations and calibration data, and plot curves by over-spectral scanning, fixed wavelength time scanning and linear regression.

8-inch color touch LCD monitor
- Adopt 8-inch color touch LCD, flexible and convenient operation, easy to read.
- High-resolution monochromator with outstanding optical precision, measurement accuracy, reproducibility, and stability.
Power failure protection measures
- Power outage protection measures can remember the measured data, scanning spectra, regression equations, and instrument correction values.
- The optional data software allows direct scanning of spectra and other processing functions, enabling mass storage of test files.
Application
The spectrophotometer is easy to operate, has perfect functions and high reliability, and can be widely used in drug testing, drug analysis, environmental testing, hygiene, and food epidemic prevention.
| Models | SISCO-L6 | SISCO-L6S |
| Optical System | Split beam, 1200 lines/mm holographic grating, C-T monochromator | |
| Display | 7 in. Touch Screen | |
| Wavelength Range | 190-1100 nm | |
| Wavelength Accuracy | ±0.5nm | |
| Wavelength Repeatability | ≤0.2nm | |
| Spectrum Bandwidth | 2nm | |
| Transmittance Accuracy | ±0.3% (T) | |
| Transmittance Repeatability | ≤0.15% (T) | |
| Transmittance Measuring Range (T) | 0.0%~200.0% (T) | |
| Absorbance Measuring Range (A) | -0.301~4.000 (A) | |
| Concentration Readout Range (C) | 0.000~9999 (C) | |
| Stray Light | ≤0.05% (T) | |
| Drifting | ≤0.0009(A)/0.5h (at 250nm and 500nm, warm up 2h) |
|
| Signal Noise | 100% T Noise≤0.15% T, 0% T Noise≤0.10% T | |
| Baseline Flatness | / | ±0.002Abs (200-1090nm) |
| Wavelength Scanning | N/A | Yes |
| Communication Port | USB | |
| Power Supply | 220V 50Hz (Optional 110V 60Hz: pls tell us by email) | |
| Overall Dimensions | 550×430×200(mm) | |
| G.W. | 23kg | |
| Software (Optional) | UV WIN8 software | |
A1: What is the difference between a UV-Visible spectrophotometer and a visible spectrophotometer?
Q1: The difference between UV-Visible spectrophotometer and visible spectrophotometer is that the measurement wavelength range is different, UV generally uses a hydrogen lamp, the measurement wavelength range is of 180 ~ 350NM, visible generally uses a tungsten lamp, and the measurement wavelength range of 320 ~ 1000NM. The so-called UV-Visible spectrophotometer also means that this instrument can change the light source, can determine the absorption peak in the UV and visible part of the compound.
A2: What is the wavelength range of the UV-Visible spectrophotometer?
Q2: Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source that illuminates the sample with light in the UV to visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometers extend the wavelength range to the near-infrared (NIR) (800 to 3200 nm).
A3: What is the principle of operation of a spectrophotometer?
Q3: The basic principle of the spectrophotometer is that the substances in solution are excited by light irradiation, resulting in the effect of light absorption, the absorption of light by substances is selective, a variety of different substances have their own absorption spectrum, so when a monochromatic light through the solution, its energy will be absorbed and diminished, the degree of light energy diminution and the concentration of substances have a certain proportional relationship, that is, in line with the colorimetric principle - -Biel's law.
Tips: How does a single-beam spectrophotometer work?
A single-beam spectrophotometer determines color by measuring the intensity of the light source before and after it is inserted into the test sample. The light source is modulated (turned on and off) to distinguish between light from the light source and light from the flame.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

