Digital Alcohol/Brix refractometer for sale online. Portable Alcohol refractometer can measure alcohol gravity with a range of 0~80%. Wine refractometer has a dual measurement range of alcohol and Brix, an alcohol range of 0~25%, and a sugar range of 0~40%. Fruit wine refractometer can measure 0~14 °Oe (Oechsle) and 0~27 KMW Babo. Beer refractometer can measure Brix scale of 0~40% and wort specific gravity of range 1.000~1.130.
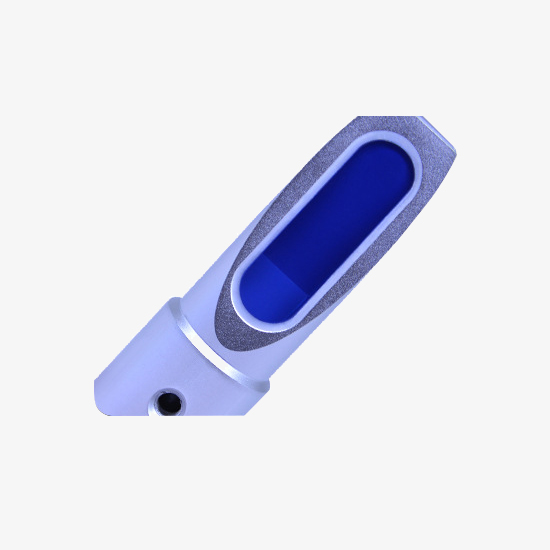

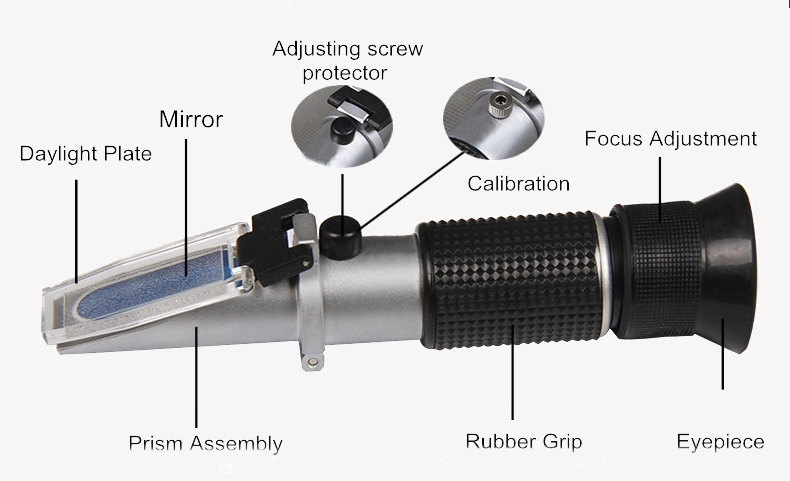
Pure Copper Movement
The pure copper movement is the core accessory of the sisco refractometer, which plays an important role in improving the durability and accuracy of the fuselage. The refractometer body is made of aluminum alloy, durable, and resistant to corrosion and dirt.
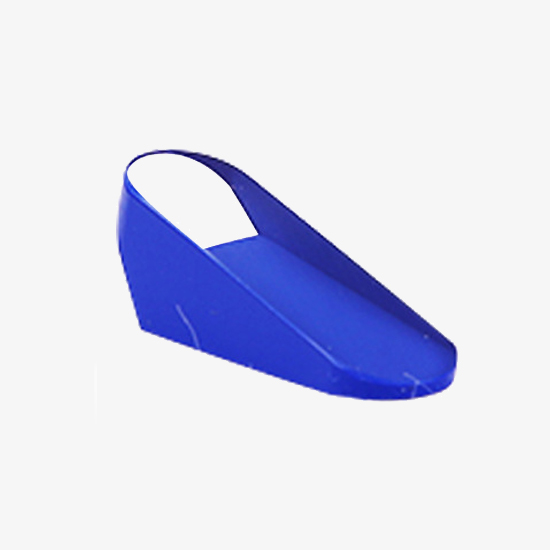

High-quality Refractometer Prisms
Precision optical prism display, high uniformity, no crack, good transparency, high dispersion, small temperature coefficient, not affected by humidity.
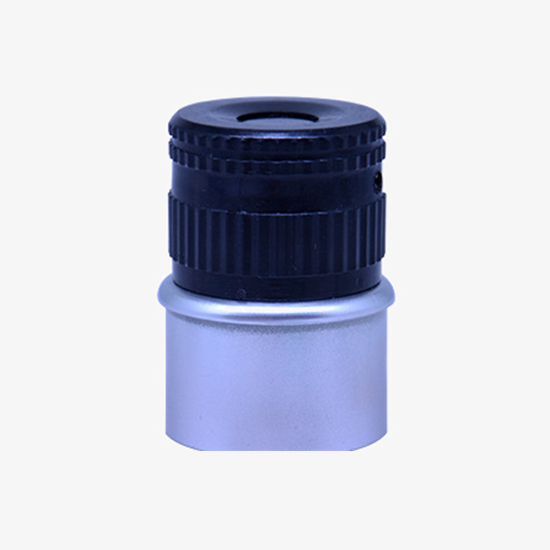

Upgrade the Eyepiece
The telescopic observation eyepiece of the Brix refractometer has adjustable focal length, long service life, clear scale display and more accurate reading.
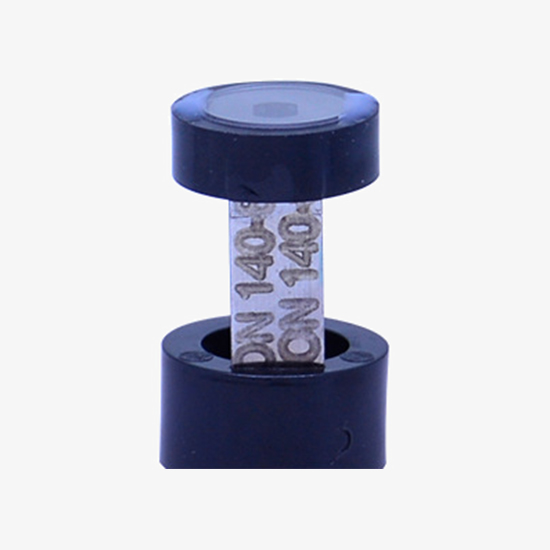

Temperature Compensation Sheet
High accuracy, with automatic temperature compensation, adopt high-quality temperature compensation sheet to avoid the influence of temperature on measurement results.
Applications
sisco digital refractometers are often used for:
- Food and beverage industry: The Brix refractometer can measure the Brix or concentration or salinity of raw materials or semi-finished products and finished products, or online detection of concentration in the production process. Test samples such as cola, fruit juice, tea drinks and other sugar-sweetened beverages, jam, honey, sugar, syrup and other sugar-sweetened foods, condiments, sauces or soups, soy milk, vegetable protein, etc.
- Flavor and fragrance industry: The portable refractive index is measured by a refractometer for qualitative inspection and judgment of purity.
- Textile printing industry: The refractometer can be used for starch determination, fixative determination, organic solvent concentration monitoring (DMF, DMSO, etc.), and slurry concentration determination.
- Chemical industry: The refractometer can measure and monitor the concentration of various organic and inorganic substances, as well as the concentration of cleaning solutions.
- Automobile transportation industry: The refractometer can measure the concentration of battery fluid, refrigerant, and snow-melting agents, such as the concentration and freezing temperature of the refrigerant in car maintenance.
- Metal processing: The coolant refractometer can monitor the concentration of cleaning fluid, cutting oil and cleaning fluid in the electronics industry.

| Model | SISCO-ALR-6080 | SISCO-BR-1130 | SISCO-WR-4025 | SISCO-FR-2732 | |||||
| Product Name | Alcohol Refractometer | Beer Refractometer | Wine Refractometer | Fruit Wine Refractometer | |||||
| Measurement Range | Alcohol | Alcohol | Brix | Wort specific gravity | Brix | Alcohol | Brix | °Oechsle | Babo |
| 0-60% V/V | 60-80% V/V | 0~32% | 1.000~1.130 | 0~40% | 0~25% V/V | 0~32% | 0~140°Oe | 0 ~ 27° KMW | |
| Minimum Division | 1% V/V | 2.5% V/V | 0.1% | >0.1% | 1% | 1% | 0.2% | 1° | 0.2° |
| Accuracy | ±1% V/V | ±2.5% V/V | ±0.1% | ±0.1% | ±0.1% | ±0.1% V/V | ±0.2% | ±1° | ±0.2° |
| Size | 30*40*205mm | 16.6*4cm (L*W) | 16.6*4cm (L*W) | 30*40*205mm | |||||
| Weight | 250g | 116g | 125g | 260g | |||||
| Temperature Compensation Range | 10℃~30℃ (50°F~86°F) | ||||||||
| Reference Temperature | 30℃ | ||||||||
| Material | Aluminium Alloy | ||||||||
| Certificate | CE | ||||||||
Package List:
- 1 x Refractometer
- 1 x pipette
- 1 x instruction manual
- 1 x mini screwdriver
- 1 x cleaning cloth
Structure Diagram
Alcohol/Brix Refractometer Use Steps
- Place a few drops of the sample to be tested onto the main prism, close the daylight plate and check the reading.
- Take the reading where the boundary line of the blue and white crosses the graduated scale.
- The scale will provide a direct reading of the concentration.
Calibration Steps
- Open the daylight plate, and place 2-3 drops of distilled water on the main prism. Close the daylight plate so the water spreads across the entire surface of the prism without air bubbles or dry spots. Allow the sample to temperature adjust on the prism for approximately 30 seconds before going to step #2. (This allows the sample to adjust to the ambient temperature of the refractometer)
- Hold the daylight plate in the direction of a light source and look into the eyepiece. You will see a circular field with graduations down the center (you may have to focus the eyepiece to see the graduations clearly). The upper portion of the field should be blue, while the lower portion should be white.
- Look into the eyepiece and turn the Calibration Screw until the boundary between the upper blue field and the lower white field meet exactly on the zero scales, as shown in the image. That is the end of the calibration process. Make sure the ambient room temperature is correct for the solution you are using (20℃/68℉). When the working temperature of the room or environment (not the sample) changes by more than5℉, we recommend recalibrating to maintain accuracy. If the instrument is equipped with an Automatic Temperature Compensation system, the ambient working temperature of the room must be 20℃ (68℉) whenever the instrument is recalibrated. Once calibrated, shifts in ambient temperature within the acceptable range (10℃~30℃ ) should not affect accuracy.
(Note: The pictures shown in the steps are only as a reference.)


Q1: What is a refractometer?
A1: A refractometer is a scientific instrument used to measure the refractive index of a substance. The refractive index is a measure of how much the speed of light changes when passing through a substance. Refractometers are commonly used in various industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceutical, chemical, and automotive industries, to name a few.
Refractometers work by shining a beam of light through a sample and measuring the angle at which the light is bent or refracted as it passes through the substance. This angle is then compared to a known scale or reference chart to determine the refractive index of the substance. Refractometers can be used to measure a variety of substances such as liquids, gases, and solids, and are particularly useful for measuring the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid sample, such as sugar content in fruit juice or wine.
Q2: How does a refractometer work?
A2: A refractometer works by measuring the extent to which a beam of light is refracted, or bent, as it passes through a sample. The amount of refraction depends on the refractive index of the sample, which is a measure of how much the speed of light changes when passing through the substance.
The basic design of a refractometer typically consists of a light source, a prism, a sample plate or well, and a detector. The prism is made of a material with a known refractive index, such as glass or plastic, and is designed to refract the incoming light beam at a specific angle. The sample is placed on the sample plate or well, and the refracted light passes through the sample before reaching the detector.
The detector measures the angle of the refracted light and compares it to a known scale or reference chart to determine the refractive index of the sample. This can be done manually by reading the scale or chart, or digitally through a display screen or computer software.
Different types of refractometers may use different methods for measuring the angle of the refracted light, such as through a handheld device, a benchtop instrument, or an inline sensor. Some refractometers also incorporate temperature compensation to account for the effect of temperature on the refractive index of the sample. Overall, refractometers are versatile instruments that can be used to measure a wide range of samples in various industries, from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and beyond.
Q3: Why do you need a refractometer?
A3: A refractometer is a valuable tool in many industries and applications because it allows for quick, accurate, and non-destructive measurements of the refractive index of a sample. There are several reasons why you might need a refractometer, including:
- Measuring dissolved solids: Refractometers are commonly used to measure the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid sample, such as sugar content in fruit juice or wine. This can be useful in industries such as food and beverage, where the quality and consistency of products depend on accurate measurements of ingredients.
- Quality control: Refractometers can be used as a quality control tool to ensure that products meet certain specifications or standards. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, refractometers can be used to check the purity and consistency of drugs.
- Research and development: Refractometers are often used in research and development to study the physical and chemical properties of substances. They can be used to investigate the refractive index of new materials, determine the composition of unknown substances, and to study the effects of temperature and pressure on the refractive index.
- Process monitoring: Refractometers can be used as inline sensors to monitor processes and ensure that they are running smoothly. For example, in the chemical industry, refractometers can be used to monitor the concentration of solutions in real time, helping to optimize production processes and reduce waste.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

