Buy a digital counter with 4 digit display, frequency/rev/linear speed measuring function, DC 12V/24V external power supply. sisco digital counters can be customized as special test instrumentation for pulse width detection, duty ratio detection, etc.
Features
- Various parameter settings, simple operation.
- Input: Various waveform pulses (square wave, triangle wave), proximity sensor, photoelectric sensor, voltage signal, contact switch, encoder, etc.
- A Digital counter can also be used to measure the power frequency (AC 0-600V), measurement range: 0.01Hz-100KHz, resolution: 0.01Hz.
- 4-digit display, decimal point automatic conversion.
- Input/output signals photoelectric isolated, anti-interference ability.
- Digital output: Up to 3 alarms, high value, low value, high and low-value alarm modes are optional, analog output: 4-20mA or 0-10V transmission output, measuring range setting arbitrarily.
- Standard RS232 or RS485 MODBUS RTU communication, can be directly connected with computers, PLC or other equipment.
Applications
In the digital system, the counter mainly counts the number of pulses to realize the functions of measurement, counting and control, and also has the function of frequency division. Digital counters are widely used in various fields, including industrial production, digital systems, traffic signal control, paper cutter positioning and elevator positioning and speed regulation.

| Mode | SISCO-DIGC-FA4 |
| Weight | 300g |
| Accuracy | 0.1%±2 digit |
| Power supply | AC 220V/110V±15%, AC 90-260V, DC 24V±10%, power dissipation≤5VA |
| Input signal | Pulse signal, square wave, sine wave, 5V≤H≤30V, 0≤L≤2V, rising edge trigger, frequency: 0.01~10KHz, 1Hz-100KHz |
| Display counting range | -1999~9999 |
| Input impedance | ≥10KΩ |
| Transmission output | 4-20mA, 0-10V, etc. (range can be set) |
| Insulation resistance | ≥100MΩ (between DC 500V power terminal and external terminal) |
| Dielectric strength | AC 1500V 1min (between power terminal and external terminal) |
| Environment | Ambient temperature: 0~50°C, relative humidity: 35~85%RH |
| External power supply | DC 12V±5%, 50mA max / DC 24V±5%, 30mA max |
| Protection class | IP65 |
Wiring diagram
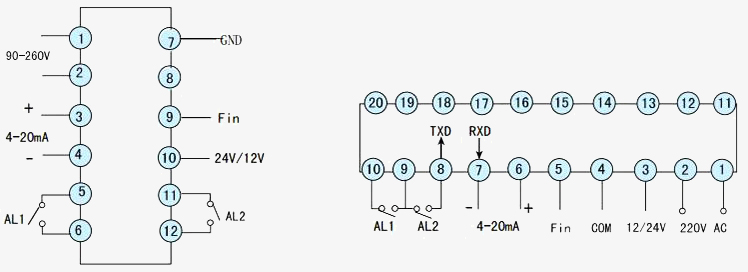
Q1: What is a digital counter?
A1: Counting is one of the simplest and most basic operations. In digital logic and computing, a counter is the logic circuit that implements this operation. In digital systems, a counter mainly counts the number of pulses for measurement, counting, control, and other functions. It also has a frequency division function. A digital counter consists of a basic counting unit and some control gates. The counting unit consists of a series of various flip-flops with the function of storing information. These flip-flops include RS flip-flops, T flip-flops, D flip-flops and JK flip-flops. Counters are widely used in digital systems. For example, in the controller of an electronic computer, the next instruction is taken out sequentially by counting the instruction address. The operation unit records the number of additions and subtractions when multiplication and division operations are performed. A counter can be used to indicate the operating status of a product. In general, it is mainly used to indicate how many copies of the product have been folded and sorted. Its main indicator lies in the number of bits of the counter, commonly 3 and 4 bits. Obviously, a 3-digit counter can display up to 999 and a 4-digit counter can display up to 9999.
Q2: How to choose a digital counter?
A2: Choosing a digital counter involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your specific needs and requirements. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
- The choice of the built-in crystal oscillator.
- The resolution of the digital counter.
- Large screen touch design.
- The counter has more measurement functions.
- Internal crystal oscillator calibration function.
- The communication interface of the counter should be as many as possible.
- Wide measuring range
Q3: What are the Types of Counters?
A3: Counters are electronic devices used to count occurrences of input signals or events. They come in various types, each designed for specific counting applications. Here are some common types of counters:
- According to whether the flip-flops in the counter are flipped at the same time, the counter can be divided into two types: synchronous counter and asynchronous counter.
- According to the increase and decrease of numbers in the counting process, the counters can be divided into addition counters, subtraction counters, and reversible counters. It is an up counter that keeps increasing with the clock signal, and a down counter that keeps decreasing. A counter that can be incremented or decremented is called a reversible counter.
The most commonly used is the first one because it allows people to know at a glance what triggering method this counter is so that designers can design circuits.
Tips: Digital counter applications in positioning and speed regulation of elevator
The leveling signal of the elevator is obtained by the position sensors installed in the elevator well. When there are many floors, the number of such signals is large, and there are certain difficulties in equipment installation and maintenance. At the same time, these signals take up a lot of PLC input ports. If using PLC and a high-speed counter for positioning, it can not only solve these problems but also can achieve frequency control of the elevator.
When the elevator is running, the digital counter completes the counting work driven by the optical encoder. When the elevator car rises, the digital counter counts up. When the elevator car goes down, the digital counter counts down. The current value of the counter is the exact position of the car in the elevator well. In this way, the accurate positioning of the elevator is realized. This positioning method has the following functions: It realizes the floor digital display of the elevator lobby and car, determines the running direction, and determines the braking time of leveling.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

