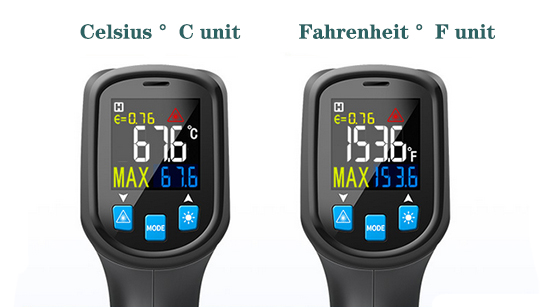
Non-contact infrared thermometer, can work in (-50°C to 400°C), (-58°F to 752°F) , power supply by AAA 7 battery*2. Optional °C/°F two units switch. Usually apply in oven, the heating, switch and refrigerator temperature measurement.
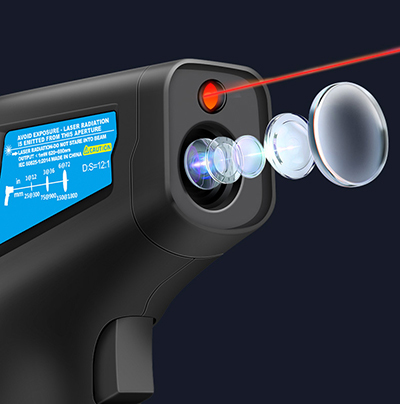

High-quality upgraded sensors, professional high and low temperature measurement, anti-interference/acceptance higher stability
- Correct measurement method
- When measuring boiling liquid, do not get close to water vapor, and keep the measurement angle at about 45-60 degrees

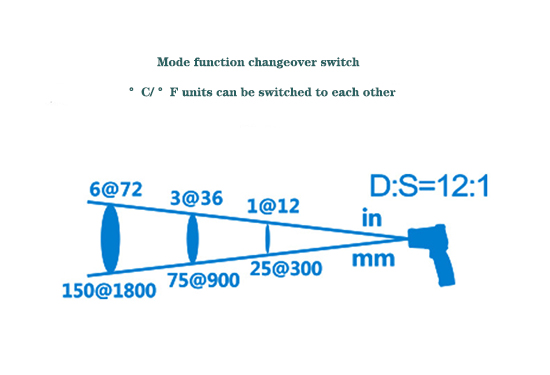
Mode function changeover switch
- Long press the mode button, adjust to °C/F unit, adjust and then press the measuring handle to measure
Details
Optional °C/°F unit switch
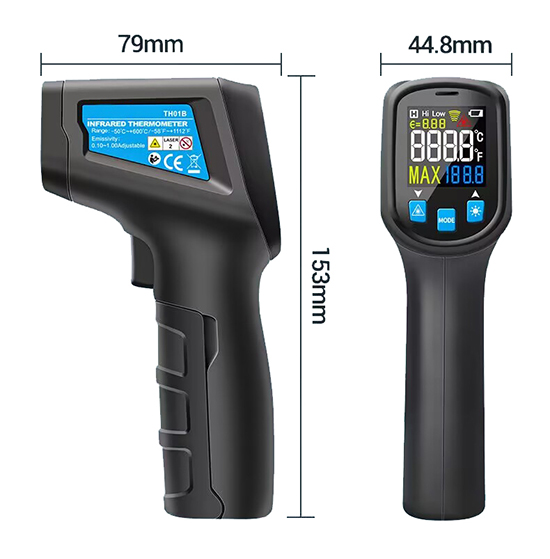
Non contact infrared thermometer size

Application
Infrared thermometers measure the surface temperature of objects, and the measurement speed responds quickly and promptly. As long as the target infrared radiation is received, the temperature can be quickly determined in a short time. It is widely used in kettles, air conditioners, light bulbs, refrigerators, ovens, heating and other daily necessities temperature measurement.


| Model | SISCO-TH01A | SISCO-THO1 B |
| Measuring range | -50°C to 400°C | -50°C to 600°C |
| -58°F to 752°F | -58°F to 1112°F | |
| Measurement accuracy | ±(1.5% of reading+2°C) | ±(1.5% of reading +2°C/4°F) |
| Emission | 0.1 to 1.0 | |
| Field of view ratio | D:S 12:1 | |
| Response time | <0.5 seconds | |
| Automatic shut-down | 30 seconds | |
| Power supply | AAA size 7 battery*2 | |
| Size | 153*79*44.8mm | |
| Net weight | 104g | |
| Type | Handheld | |
| Display method | LCD | |
| Battery type | AAA*2 | |
| Material | ABS | |
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.
Q1: What is infrared thermometer?
A1: Infrared thermometer is a temperature measuring instrument based on the principle of infrared rays. This kind of temperature measuring instrument can measure the temperature by the length of infrared rays. Infrared thermometer is a kind of measuring instrument, which can realize short-distance measurement and long-distance measurement, and is a kind of temperature-measuring instrument that can be used in various environments.
Q2: How does infrared thermometer work?
A2: Infrared radiation is the most widespread electromagnetic wave radiation in nature. Objects with a temperature above absolute zero will radiate infrared rays due to their own molecular motion. After the power signal radiated by the object is converted into an electrical signal by the infrared detector, the output signal of the imaging device can completely simulate the spatial distribution of the surface temperature of the scanned object one by one. After being processed by the electronic system, it is transmitted to the display screen and obtained the thermal image corresponding to the heat distribution on the surface of the object.
Q3: What is infrared thermometer used for?
A3: Today, infrared thermal imaging systems have been widely used in fields such as electric power, fire protection, petrochemical and medical treatment. Infrared thermal imaging cameras are playing a pivotal role in the development of the world economy.
Tips: What should we pay attention to when use infrared thermometer?
- Determine the temperature measurement range: The temperature measurement range is the most important performance index of the thermometer. Some thermometer products have a range of -50°C to +3000°C, but this cannot be done by one type of infrared thermometer. Each type of thermometer has its own specific temperature range. Therefore, the user's measured temperature range must be considered accurately and comprehensively, neither too narrow nor too wide.
- Determine target size. Infrared thermometers can be divided into single-color thermometers and two-color thermometers (radiation colorimetric thermometers) according to the principle. For a monochromatic thermometer, when measuring temperature, the area of the target to be measured should fill the field of view of the thermometer. It is recommended that the measured target size exceed 50% of the field of view. If the target size is smaller than the field of view, the background radiation energy will enter the visual and acoustic symbols of the thermometer and interfere with the temperature measurement readings, causing errors.
- Determining the distance factor (optical resolution). The distance coefficient is determined by the ratio of D:S, that is, the ratio of the distance D between the probe of the thermometer to the target and the diameter of the target to be measured. If the thermometer must be installed far away from the target due to environmental conditions, and a small target must be measured, a thermometer with high optical resolution should be selected. The higher the optical resolution, i.e. increasing the D:S ratio, the higher the cost of the pyrometer.

