The provided thermocouple is used for temperature measurement of liquid temperature, and gas temperature. Thermocouple thermometer offers 800mm length, 0~1000°C measuring range, and a waterproof and rust-proof junction box. Works with a display instrument, recording instrument and electronic regulator, K-type thermocouple is widely used in the chemical industry, petroleum, machinery, shipbuilding, power generation, etc.
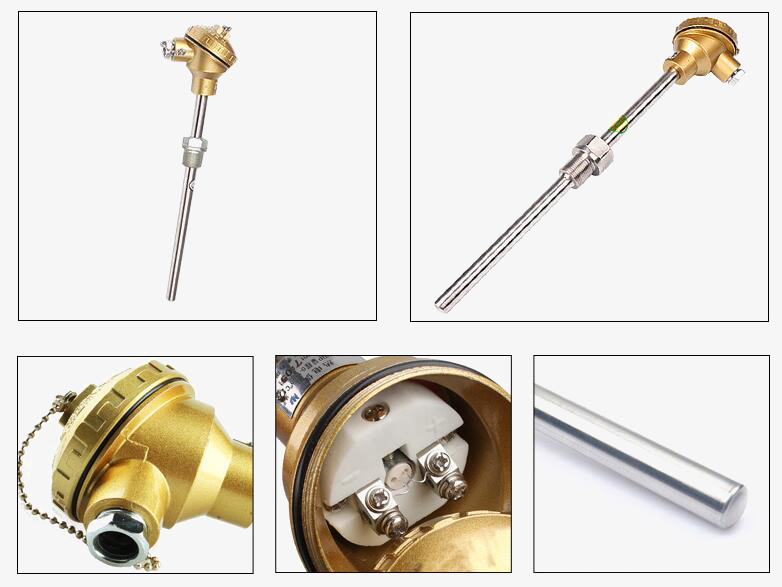

K-type thermocouple is used for temperature measurement of liquid temperature, and gas temperature, and are widely used in the chemical industry, petroleum, machinery, shipbuilding, power generation, textile, printing and dyeing, etc.
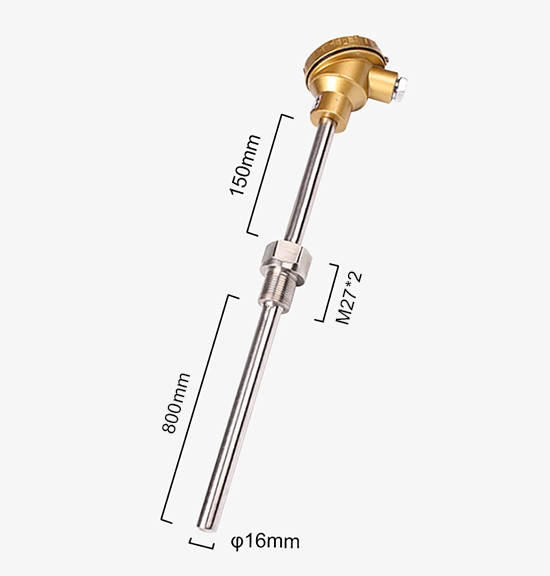
- The 800mm thermocouple is the most commonly used temperature detector in medium and low-temperature areas, equipped with a high-temperature resistant thermocouple head, high-frequency anti-interference, and temperature resistance 0-1000°C.
- The thermocouple has a waterproof and rust-proof junction box, stable, strong, durable, and long service life.
- The interior of the thermocouple thermometer uses high-frequency magnetic beads for more precise use.
- Both a two-wire system and a four-wire system can be selected, and the measurement is more stable.
- The German back cover technology is adopted, and the thermocouple thermometer is shock-resistant and pressure-resistant.
Details
Applications
SISCO K type thermocouples are widely used in science and industry, including temperature measurement for kilns, gas turbine exhaust, diesel engines, and other industrial processes. Thermocouples are also used in homes, offices and businesses as temperature sensors in thermostats, and also as flame sensors in safety devices for gas-powered major appliances.

- Model: SISCO-WRN-230-K800
- Range: 0-1000°C
- Thread: M27*2
- Length: 800mm
- Even Wire Diameter: Default 2.5mm
- Installation Method: Fixed Thread device
- Protective Tube Diameter: Default 16mm
- Protective Tube Material: Default 304
Note:
- Thread, insertion depth and cold end length can all be customized. If necessary, please contact us.
- Use 2520 high-temperature resistant material or 310 stainless steel protection tube for long-term temperature measurement above 1000 degrees, and the diameter of the dual wire is 2.5mm or 3mm.
Q1: What is a thermocouple?
A1: A thermocouple is a commonly used temperature-measuring component in a temperature-measuring instrument. It directly measures the temperature and converts the temperature signal into a term electromotive force signal, which is converted into the temperature of the measured medium by an electric meter (secondary meter). The shape of various thermocouples is often very different due to the needs, but their basic structure is almost the same, usually composed of the hot electrode, insulating sleeve protection tube and junction box, etc., usually with a display instrument, recording instrument and electronic adjustment Used in conjunction with the device.
Q2: What is a K-type thermocouple used for?
A2: As a transmitter for measuring temperature, industrial K-type thermocouples are usually used in conjunction with display instruments, recording instruments and electronic regulators. It can directly measure the surface temperature of liquid, vapor and gaseous media and solids ranging from 0°C to 1000°C in various production processes.
Q3: How does a thermocouple work?
A3: A thermocouple is the connection of two different conductors or semiconductors into a closed circuit. When the temperature of the two junctions is different, an electromotive force will be generated in the circuit. This phenomenon is called the hot spot effect, also known as the Seebeck effect. The end directly used to measure the temperature is called the working end, and the other end is called the cold end. The cold end is directly connected to the instrumentation or supporting equipment, and the display instrument will point out the electromotive force generated by the thermocouple.
Tips: Thermal Resistance vs. Thermocouple
- Different thermometry principles
Thermal resistance: Thermal resistance measures temperature based on the thermal effect of resistance, and the resistance value of the resistance body changes with temperature. Therefore, as long as the resistance change of the thermal resistance is measured, the temperature of the object can be measured.
Thermocouple: The principle of thermocouple temperature measurement is based on the thermoelectric effect. The thermoelectromotive force generated by the thermocouple only changes with the temperature of the hot end (measurement end), which means that a certain thermoelectromotive force corresponds to a certain temperature. Therefore, the purpose of temperature measurement can be achieved as long as the method of measuring thermal electromotive force is used. - Different temperature ranges
Thermal resistance: low temperature detection, thermal resistance generally detects the temperature range of -50~300°C.
Thermocouple: for high temperature detection, the thermocouple can detect the temperature range of -200°C to 1300°C, and in special cases -270°C to 2800°C. - Different materials
Thermal resistance: Thermal resistance is a metal material that has a temperature-sensitive change.
Thermocouple: A thermocouple is a bimetallic material, that is, two different metals. Due to changes in temperature, a potential difference is generated at both ends of two different metal wires. - Different signals
Thermal resistance: The thermal resistance itself is a resistance, and the temperature change causes the resistance to produce positive or negative resistance changes.
Thermocouple: A thermocouple produces a change in induced voltage that changes with temperature.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

