Portable gas detector provides high precision detection for CO gas with the range of 0-500ppm, 0-1000ppm, and 0-2000ppm. Handheld design, audible, visual and vibrating alarm, light weight and small size, easy to carry everywhere with a clip, carbon monoxide detector is suitable for oil, metallurgy, chemical, medical, agriculture, refinery and other industries.
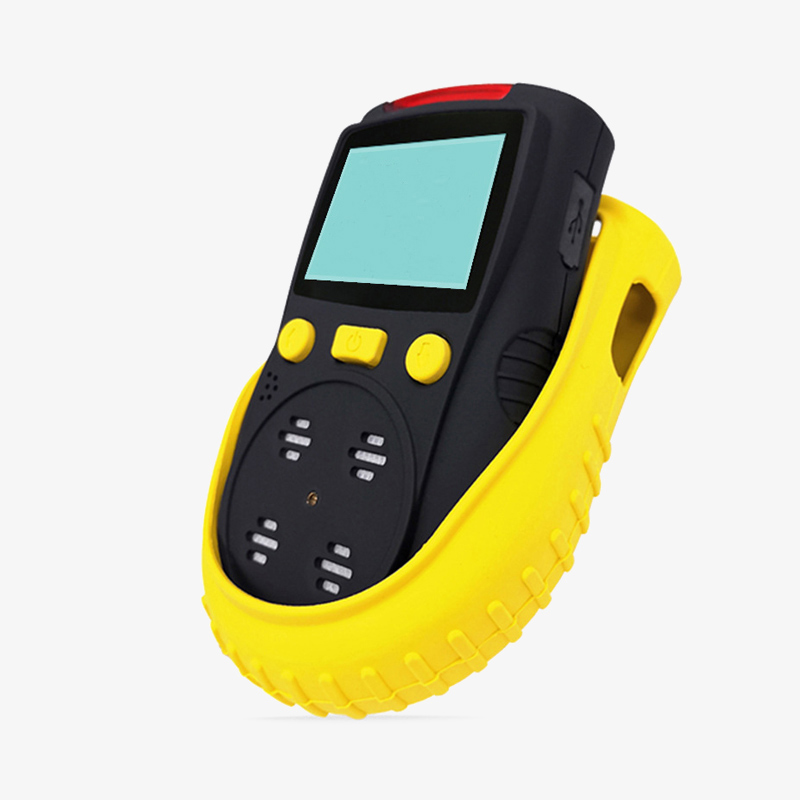

Portable gas detectors can detect carbon monoxide (CO) quickly.
- The gas detector is available with an LCD dot matrix display and Chinese and English operation modes.
- The gas concentration unit PPM and mg/m3 can be shifted quickly.
- The battery and voltage can be checked with one press.
- One press to restore factory settings.
- Ultra-high buzzer alarm sound, alarm with sound, light and vibration at the same time.
- Rechargeable lithium polymer battery of large capacity, which ensures the gas detector works continuously for a long time.

Adopts high-precision sensor/Provides data storage function
- The portable carbon monoxide detector employs the original imported high-precision sensor.
- sisco handheld CO detector can record 100 sets alarm data, alarm record can be checked on the device.
- Data storage function, gas detector can record 100 thousand set data, and historical data can be viewed on the device (optional function).
- Strong and upscale alligator clip, convenient to take along during operation.
- Special engineering plastics housing of high intensity, strong and durable, exquisite and comfortable in touch.
Details
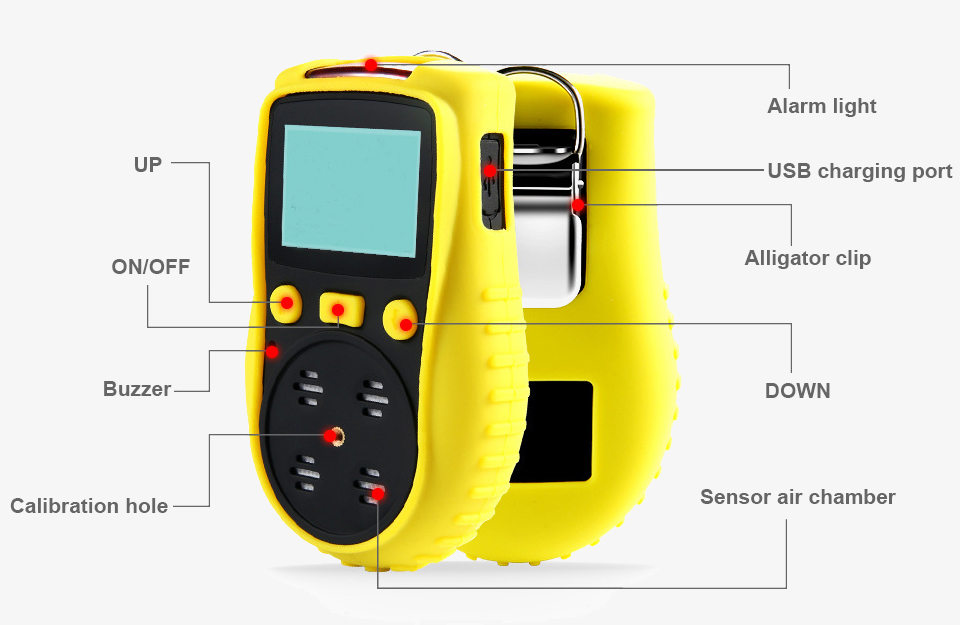
Applications
sisco portable carbon monoxide detector is used to measure CO concentration and alarm in confined spaces in tunnels, sewers, underground shafts, mines, cement plants, thermal power plants, agriculture, oil refinery and other industries to effectively prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.

| Model | GD500-CO |
| Sampling Method | Diffusion |
| Gas | Carbon Monoxide (CO) |
| Range | 0 to 500 ppm, 0 to 1000 ppm or 0 to 2000 ppm (Optional) |
| Resolution | 1ppm |
| Accuracy | ≤±3%F.S. |
| Display | Monochrome dot matrix 128*128 LCD graphic display |
| Backlight | Backlight time is settable; the backlight will be auto on when alarming. |
| Data Logging (Optional Function) | Storage capacity of over one hundred thousand sets. Interval time ranginf from 10~3600 seconds are settable. |
| Alarms | Sound, light and vibration |
| Operation Language | Chinese/English |
| Gas Unit | Gas units ppm and mg/m3 are switchable |
| Battery | 3.7V rechargeable lithium battery with 2300mAh capacity Operating time about 10-12h |
| Charger | Travel charger with USB. Typical charge time 4-6 hours. |
| Explosion-proof Grade | Exia ll CT3 |
| Case Material | ABS+PC |
| Protection Grade | IP65 |
| Operating Temperature | -20℃~50℃ |
| Operating Humidity | 0~90%RH (non-condensing) |
| Dimension | 131*85*35mm |
| Weight | 240g |
Gas Detector Catalog & User Manual
 SISCO Gas Detector Catalogue
SISCO Gas Detector Catalogue SISCO GD200 Portable Gas Detector User Manual
SISCO GD200 Portable Gas Detector User Manual SISCO GD300 Online Fixed Gas Detector User Manual
SISCO GD300 Online Fixed Gas Detector User Manual SISCO GD400 Explosion Proof Portable Gas Detector User Manual
SISCO GD400 Explosion Proof Portable Gas Detector User Manual SISCO GD500 Handheld Multi Gas Detector User Manual
SISCO GD500 Handheld Multi Gas Detector User Manual SISCO GD600 Multi Gas Analyzers User Manual
SISCO GD600 Multi Gas Analyzers User Manual SISCO Gas Detector Communication Protocol V1.0
SISCO Gas Detector Communication Protocol V1.0 SISCO Single Stage Pressure Regulator User Manual
SISCO Single Stage Pressure Regulator User Manual SISCO Gas Detector Data Downloading Operation Instruction
SISCO Gas Detector Data Downloading Operation Instruction
Gas Detector Software
Q1: What is a gas detector?
A1: A gas detector is an instrument for gas leakage concentration detection, including a portable gas detector, handheld gas detector, fixed gas detector, online gas detector, etc.
Q2: What does a gas detector detect?
A2: Combustible gases: Natural gas (methane), liquefied gas, coal gas (hydrogen), acetylene, pentane, alkynes, acetone, toluene, alcohols, hydrocarbons, light oil, etc.
Toxic gases: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, chlorine, oxygen, phosphine, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, chlorine dioxide and other toxic and harmful gases.
Q3: What is ppm of gas detector?
A3: Parts per million or "ppm" is often used as a fractional measure of concentration. For example, a methane (molecular) concentration of 2% means that 2 out of every 100 air molecules are methane. Likewise, a methane concentration of 2 ppm means that 2 out of every 1 million air molecules are methane.
Tips: What do the units PPM, %LEL, %VOL mean in the gas detector?
- PPM: PM refers to parts per million, a unit of gas volume concentration.
For solution: it means that there’s 1/1000 ml solute in the 1L aqueous solution, so its concentration is 1ppm.
For gas: it’s one of the representation methods of pollutant concentration in the ambient atmosphere (air). - %LEL: LEL refers to the lower explosive limit. When the combustible gas reaches 100%LEL, it’s easy to explode, and the explosion occurs as soon as contacting an electric spark. Therefore, 0-100%LEL generally refers to the range of combustible gas measurement. For example, hydrogen: 4%VOL=100%LEL, methane: 5%VOL=100%LEL.
- %VOL: VOL refers to the volume ratio of target gas per volume. It’s generally used for high concentration. 1%VOL is equal to 10000PPM, and generally, it is for oxygen and combustible gases.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

