High-accuracy digital storage oscilloscope with 70 MHz bandwidth, 1 GSa/s sampling rate, 8 inches large LCD screen. The professional portable oscilloscope with an FFT display function can analyze the spectral characteristics of the signal. Cursor measurement function, convenient manual measurement period, frequency, and voltage.
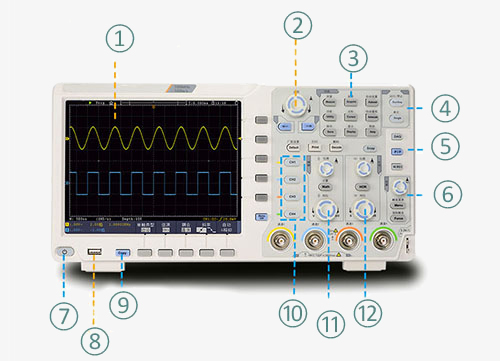
Digital storage oscilloscope interface details
- 8-inch high-resolution LCD screen
- Rubberized knobs
- Common function selection area
- Executive control
- Optional functional area
- Trigger easter egg area
- Switch
- Front USB copy button
- Copy button
- Channel selection button
- Disposal control area
- Horizontal control area
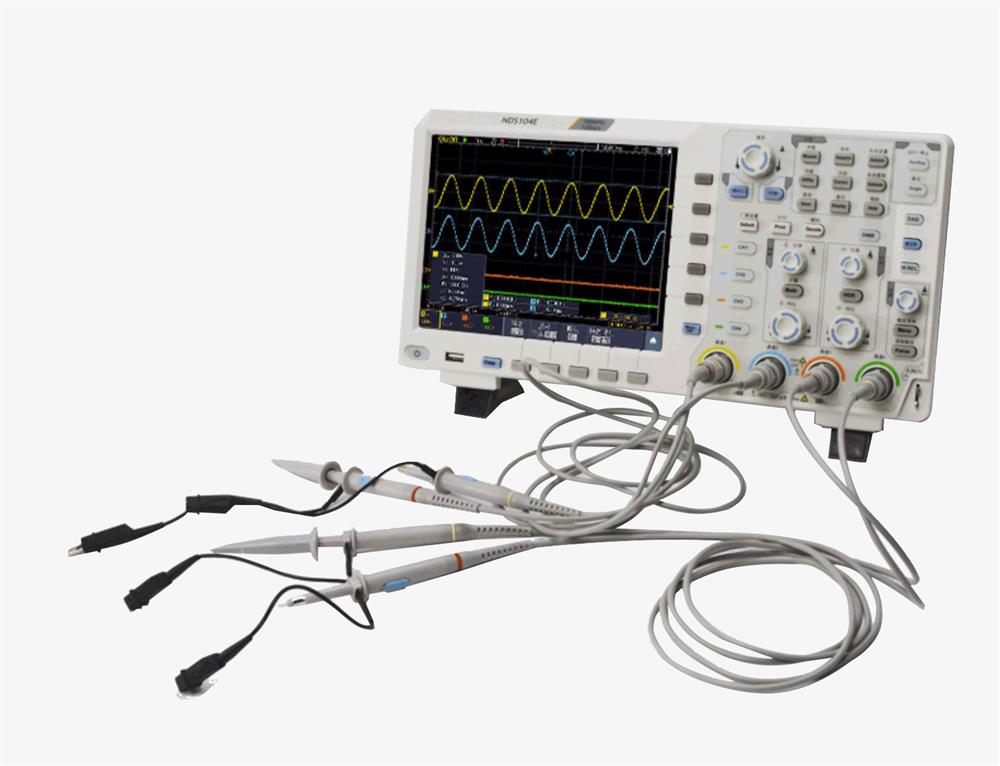
The passive probe as standard
- Better durability
- Four-channel input
- Multi-level grayscale and color temperature display
Application
The main application of a SISCO oscilloscope is used to display the waveforms of signals. It can be used in many fields such as automotive test, signal analysis, electrical, transducer test and measurement, electrical equipment design, medical equipment testing field, etc.

| Model | SISCO-NDS-074E |
| Bandwidth | 70 MHz |
| Channel | 4 Channel |
| Sample rate | 1 GSa/s |
| Acquisition model | Sample, Peak detect |
| Record length | 40M |
| Display | 8 inch LCD |
| Waveform refresh rate | 45000 wfrms/s |
| Input coupling | DC, AC, Ground |
| Probe attenuation | 1X, 10X, 100X, 1000X |
| Input Impedance | 1MΩ ± 2%, in parallel with 15pF ± 5pF |
| Max. input voltage | 400V (DC+AC, PK - PK) |
| Sampling rate range | 2ns/div ~ 1000s/div, step by 1-2-5 |
| Vertical Resolution | 8 bits |
| Sensitivity Resolution | 2mV/div~10V/div |
| Low Frequency(-3db) | ≥5 Hz (at input, AC coupling) |
| Rise time (at input, Typical) | ≤5ns |
| Trigger type | Edge |
| Trigger model | Auto, Normal, Single |
| Trigger level range | ±6 div from the screen center |
| Automatic measurement | Vpp, Vavg, Vrms, Frequency, Period, Vmax, Vmin, Vtop, Vbase, Vamp, Overshoot, Preshoot, Rise Time, Fall Time, +Width, -Width, +Duty, -Duty, DelayA→B , DelayA→B |
| Cursor measurement | ΔV, ΔT, ΔT&ΔV between cursors,auto cursor |
| Dimension | 340*177*90mm |
| Weight | 2.6kg |
Accessories
- Power cable
- USB cable
- Probe
- Probe Adjust
- Quick Guide
Q1: Can an oscilloscope measure DC voltage?
A1: DC voltage can be measured using either an oscilloscope or a digital multimeter. Each piece of testing equipment has its advantages and disadvantages.
Q2: What is the maximum frequency for the oscilloscope?
A2: System bandwidth determines an oscilloscope's fundamental ability to measure an analog signal - the maximum frequency range that it can accurately measure. Entry-level scopes will often have a maximum bandwidth of 100 MHz. They can accurately (within 2%) show the amplitudes of sine-wave signals up to 20 MHz.
Q3: What is the record length for an oscilloscope?
A3: The record length, measured in points or samples, divided by the sample rate (in Samples/second) specifies the total time (in seconds) that is acquired. Example: With a record length of 1 M points and a sample rate of 250 MSa/sec, the oscilloscope will capture a signal of 4 msec in length.
Tips: What does the sampling rate mean for a digital oscilloscope?
The sampling rate is an important index of a digital oscilloscope. The sampling rate is also called the digitization rate. It refers to the sampling time of analog input signal in unit time and is often expressed in MS/s. If the sampling rate is not enough, aliasing is prone to occur.
If the oscilloscope's input signal is a 100KHz sine signal, the oscilloscope's display signal frequency is 50KHz. What's going on here? This is because the oscilloscope's sampling rate is too slow, resulting in aliasing. Aliasing is when the waveform frequency displayed on the screen is lower than the actual frequency of the signal, or the displayed waveform is unstable even if the trigger indicator on the oscilloscope is on.
So, how do you determine if the waveform shown has been duplicated for a waveform of unknown frequency? The frequency parameters of the waveform can be changed rapidly by changing the sweep t/div to the faster time base. If it is, the waveform mixing has occurred. Or the swaying waveform stabilizes at a faster time base, indicating that the waveform alias has occurred. According to Nyquist, the sampling rate is at least 2 times higher than that of the signal high-frequency component, and it will not occur. For example, a 500MHz signal requires at least a 1GS/s sampling rate.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

