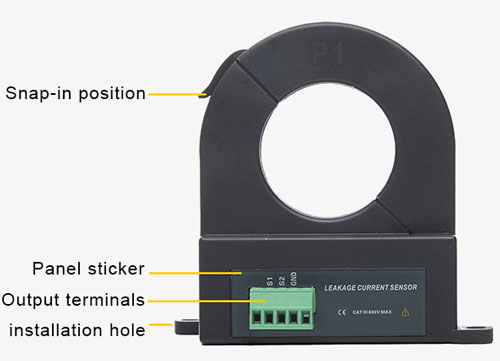
The 60A split core current transformer uses double shielding technology to ensure the stability and reliability of uninterrupted measurement, with an opening and closing size of 40mm, a ratio of 800:1 and an operating frequency of 10Hz~100KHz, which can be used for data logging, energy management and power monitoring.
Non-contact measurement is convenient, fast, and safe.
- Open-close structure, no need to disconnect the measured line without power failure, especially suitable for online installation. Non-contact measurement, is convenient, fast, and safe.
- sisco split core current transformer adopts PoMo alloy core, CT double shielding technology, stable performance and high precision, strong anti-interference ability, suitable for complex interference environment.
- The range, ratio, and output interface of the sensor can be customized according to customer requirements.
- A split core current transformer enables to clamp of the fire wire and zero wire together to measure the leakage current of cable wires and electrical equipment.
- The split core current transformer is available with either a current signal or a voltage signal.
Application
High-precision split current transformers are an indispensable accessory for small, medium, and large electronic companies. The sisco slip current transformer is suitable for use in power equipment testing, communications and telecommunications, railway and oilfield monitoring, building and construction companies, research and teaching units, industrial and mining records, and other fields.

| Model | SISCO-ETCR040K |
| Range | 0.00mA~60A AC |
| Resolution | 0.01mA AC |
| Accuracy Grade | 0.5 |
| Phase Error | ≤2° |
| Variable Ratio | 800:1 |
| CT Size | φ10mm |
| Secondary Load | ≤10Ω |
| Shielding | Double shielding, suitable for complex interference environment |
| Output Mode | Induction current output |
| Output Interface | 2-core shielded line 2M |
| Frequency | 10Hz~100KHz |
| Safety Level | CATI600V |
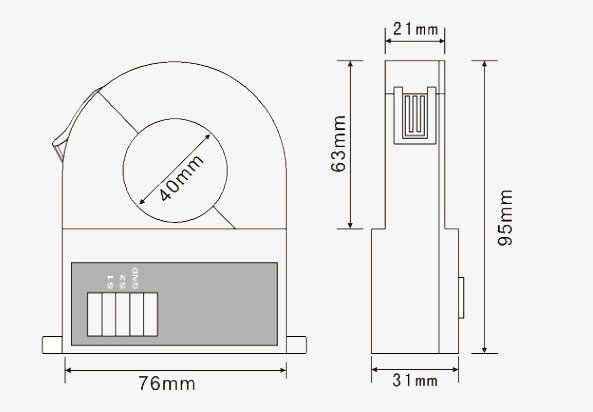
| Dimension | 95mm x 98mmx 31mm |
| Mass | 160g |
| Working Temperature | -15°C~ 50°C |
| Dielectric Strength | AC 3700V/rms (between core and case) |
Dimension Unit (mm)
Q1: What is a split-core current transformer?
A1: Split core current transformer is made of high strength PVC shell, fully cast busbar type structure. a split core current transformer is directly stuck on the cable with three sexual rubber rings against the cable and the cable one. The transformer core uses better silicon steel rolled, the secondary wire evenly wound in the core. Transformers for the open and closed structures can be installed without cutting the cable.
Q2: What is the meaning of the circles of the split core current transformer?
A2: On electrical system diagrams, a small circle is often used to represent a winding, and a circle is used to represent a winding. If you have two circles in a series, that means that the open and closed current transformer has two windings. If you have three circles in a series, that means you have three windings.
Q3: What is a split core current transformer error?
A3: Due to the structure of the split core current transformer core and material properties, the current transformer has an excitation current I0, which makes it produces errors.
Tips: What is the difference between split core current transformer AC and DC?
- Core
The core of the AC open/closed current transformer is made of mutually insulated silicon steel sheets, which are double E-shaped. Most of the DC cores are integral soft iron, most of which are u-shaped. - Arc extinguishing system
The current transformer adopts a magnetic blow-out device, AC current transformer adopts a magnetic blow-out device. - Number of turns of the coil
AC transformer coil turns less, with small resistance, and DC open current transformer coil turns more in DC, AC contactor in the AC circuit, DC contactor in the DC circuit. AC working frequency 600 times/hour, low cost. DC working frequency up to 2000 times/hour, high cost of use.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

