High voltage tester is a kind of instrument used to test the insulation strength of electrical equipment, widely used in electric power, electronics, communications and other fields. sisco online shop will introduce the working principle of high voltage tester in detail.
Principle of Operation
The working principle of a high voltage tester is mainly based on the phenomena of electric field and electric breakdown. When the HV tester is switched on, the low-voltage power supply is boosted by a transformer to the high voltage required for the test and then the high voltage is applied to the object under test. Next, depending on the insulation strength of the object under test, the high voltage tester detects the change in current and gives the result of the test via a display or indicator.
The Role of the Electric Field
The electric field is the basis for the operation of a high-voltage tester. When high voltage is applied to a test object, an electric field is formed. The effect of the electric field is to separate the charges so that positive and negative charges are distributed within the object under test. This separation effect can be realized by the electrodes of the high voltage tester, which are divided into high voltage and ground electrodes, and the distribution of the electric field is adjusted by the distance and shape between the electrodes.
Electric Breakdown Phenomenon
Electrical breakdown occurs when the electric field strength reaches a certain level. Electrical breakdown means that the electric field strength exceeds the insulation strength of the object under test, resulting in an electric charge passing through the insulation layer of the object under test and forming a discharge path. At this point, the high voltage tester will detect the change of current, so as to judge whether the insulation strength of the object under test is qualified or not.
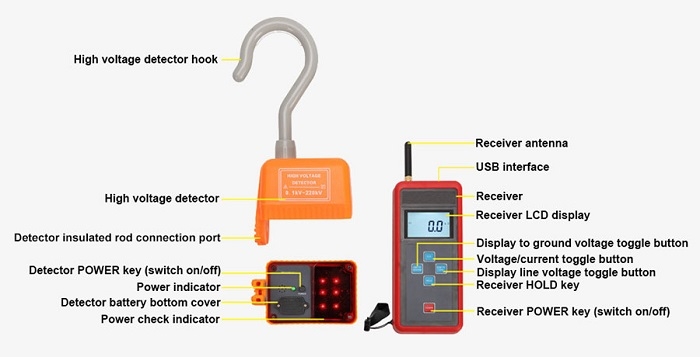
Key Functions and Applications
- Voltage Measurement
The primary function of high-voltage testers is to measure the voltage in high-voltage systems accurately. They are capable of measuring voltage levels that standard voltage testers cannot handle. - Insulation Resistance Testing
High-voltage testers are used to assess the insulation resistance of electrical components and cables. This test helps identify potential weaknesses or faults in the insulation, which can lead to electrical breakdowns. - Dielectric Strength Testing
These testers are used to determine the dielectric strength of insulating materials. The dielectric strength is the maximum voltage an insulating material can withstand without breaking down. - Continuity Testing
High-voltage testers can check the continuity of conductors and connections in high-voltage systems to ensure they are intact and functioning as intended. - Hipot Testing (High-Potential Testing)
Hipot testing is a type of high-voltage testing used to assess the electrical integrity of insulation and conductors by applying a higher-than-normal voltage. It helps detect insulation defects and weaknesses.
Working Steps
- Setting up the test parameters
Before performing the high voltage test, it is necessary to set up the parameters required for the test, such as the test voltage, the test time, and so on. These parameters are determined according to the characteristics of the object to be tested and the test requirements. - Applying High Voltage
After setting up the test parameters, the high voltage tester will step up the low voltage power supply to the set test voltage through the transformer and apply the high voltage on the tested object. - Detecting current
Once the high voltage is applied to the object under test, the high voltage tester will detect the change of current by means of an ammeter or a sensor. If the current exceeds the set threshold, it means that an electrical breakdown has occurred on the object under test. - Display of test results
The high voltage tester will feedback the test results to the operator through the display or indicator light. Typically, a passing test result will be shown by a green or normal indicator light, while a failing result will be shown by a red or warning light.
Precaution
- Safe operation
The high voltage tester involves high voltage current, the operator should wear insulated gloves and other necessary protective equipment to ensure safety. - Correct selection of test voltage
The test voltage should be selected according to the requirement of insulation strength of the object to be tested, too high test voltage may lead to electric breakdown or damage to the object to be tested. - Reasonable setting of test time
The test time should be determined according to the characteristics of the object to be tested and the test requirements, too short a test time may not be able to accurately detect the insulation strength. - Regular calibration and maintenance
High-voltage testers should be regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure the accuracy of the test results and the reliability of the instrument.
Through the above introduction to the working principle of the high voltage tester, we can see that the high voltage tester is an instrument that judges the insulation strength of the tested object by applying high voltage and detecting current. Reasonable use and maintenance of high voltage testers can ensure the safe operation of electrical equipment.

