Nuclear radiation is also called ionizing radiation or radioactivity. Radioactive substances emit a kind of energy in the form of waves or particles called nuclear radiation, which is colorless and tasteless, i.e., invisible and untouchable, and we are unable to perceive its existence. It is colorless and tasteless, i.e., invisible and intangible, and we cannot sense its presence. It must be measured and perceived by specialized instruments. A nuclear radiation detector is an instrument used to measure and monitor the level of nuclear radiation, which has important applications in a number of fields. sisco.com will describe why we need nuclear radiation detectors.
What is Radioactivity
Radioactive decay radioactivity is the spontaneous release of radiation from the nucleus of an atom. An atom consists of a central nucleus that contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons. In a stable atom, forces within the nucleus keep it intact and prevent any spontaneous release of particles or energy.
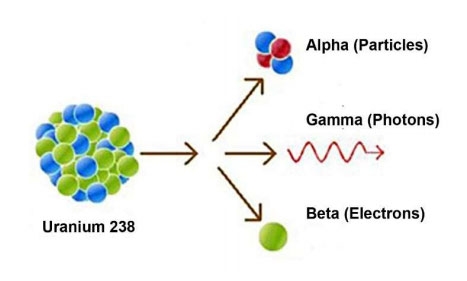
In some atoms, however, the nucleus may be unstable due to an imbalance in the number of protons and neutrons or other factors. This instability leads to a process known as radioactive decay. In this process, the unstable nucleus undergoes a spontaneous transformation to a more stable state. During the process, the nucleus emits different types of radiation. The three types of radiation emitted by radioactive decay.
An Alpha Particle (α): Consists of two protons and two neutrons and is essentially the same as the nucleus of a helium atom. alpha particles are positively charged and are relatively large and heavy.
Beta Particles (β): Beta particles can be either electrons (β-) or positrons (β+). β - particles are essentially high-speed electrons, while β + particles are positively charged electrons, also known as positrons.
Gamma Rays (γ): Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation similar to X-rays but with higher energy. They have neither mass nor charge but are very penetrating.
Effects of Radiation on Human Health
The amount of radiation exposure that is harmful to human health depends on the type of radiation, the energy of the radiation, the duration, and the sensitivity of the individual to the radiation. In general, continued exposure to low levels of radiation may increase the risk of cancer or other long-term effects. Exposure to high levels of ionizing radiation such as radiotherapy or nuclear accidents can cause acute effects such as radiation sickness.
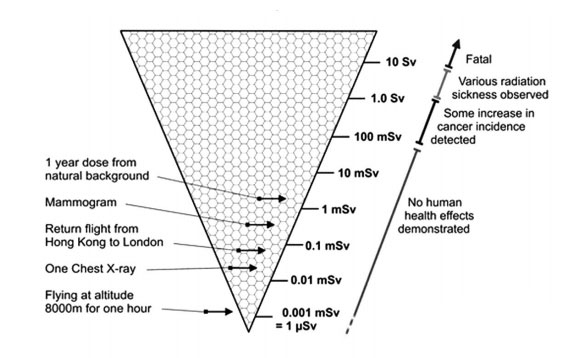
Radiation dose is the amount of radiation absorbed by an organism over a period of time. The dose of radiation a person receives determines the extent of the damage. Small doses of energy do not cause immediate cellular damage. However, larger doses can cause DNA damage. Radiation doses are measured in sieverts (Sv) or, in smaller units, millisieverts (mSv). Exposure below 100 mSv is considered low risk, 100-500 mSv is moderate risk, and exposure above 500 mSv is high risk.
The Need for Nuclear Radiation Detectors
- Monitoring in the Nuclear Power Industry: Nuclear power plants, nuclear reactors, and nuclear material processing facilities require constant monitoring of nuclear radiation levels in the environment to ensure operational safety and to prevent radioactive leakage. Nuclear radiation detectors are used to monitor the release of radioactive material in real-time.
- Radiation Safety: In the aftermath of a nuclear accident, radiation incident, or nuclear terrorism event, high quality nuclear radiation detectors are used to assess radiation risk, protect personnel from radiation exposure, and guide emergency response.

- Medical Applications: Nuclear radiation detectors are needed in the fields of nuclear medicine and radiation therapy to measure radioisotope radioactivity levels and ensure the safety of patients and medical professionals.
- Nuclear Material Tracking: Nuclear radiation detectors are used to monitor and detect the illegal transportation or misuse of nuclear materials to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and acts of nuclear terrorism.
- Environmental Monitoring: Nuclear radiation detectors are used to monitor radioactive contamination in the environment such as soil, water, and atmosphere to ensure environmental quality and food safety.
- Scientific Research: Nuclear radiation detectors are widely used in nuclear physics experiments, nuclear astronomy research, and radiation ecology research to measure and analyze radioactive particles and radiation phenomena.
- Nuclear Waste Management: Nuclear radiation detectors are used to monitor and control the handling and storage process of nuclear waste to ensure that the waste does not pose a hazard to the environment and the public.
- Radiation Vaccine Response: In the aftermath of a nuclear accident or radiation incident, nuclear radiation detectors are used to assess the radiation exposure of people and areas for appropriate emergency response measures, including evacuation and medication.
Nuclear radiation detectors are critical instruments used to ensure the safe operation of the nuclear energy industry, protect against nuclear terrorism, protect human health and the environment, and conduct scientific research. When confronted with the potential risks of nuclear radiation, radiation detectors provide timely monitoring and data that enable us to take the necessary measures to mitigate potential dangers.

