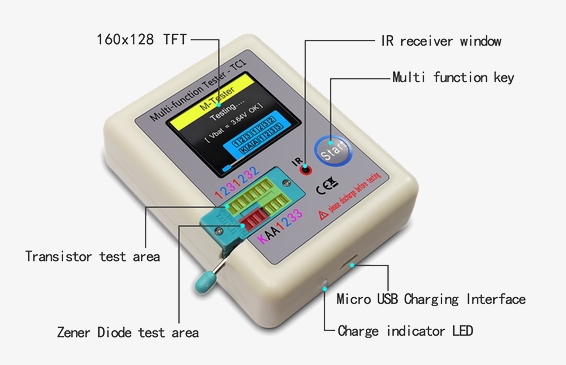
This transistor meter handles transistors, diodes, thyristors, MOSFETs, resistors, capacitors, and inductors with precision., is the ideal tool for any electronics enthusiast or professional looking to save time and ensure accuracy in their work.
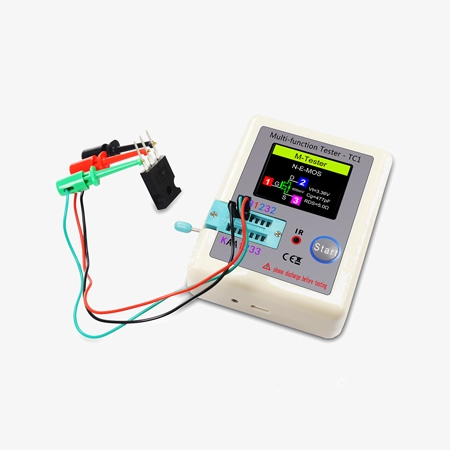

- Transistor Identification: Automatically identifies NPN, PNP transistors, MOSFETs, and thyristors.
- Diode Testing: Accurately tests diodes, including forward voltage drop and reverse bias characteristics.
- Capacitance Measurement: Measures capacitors ranging from picofarads (pF) to millifarads (mF).
- Resistance Measurement: SISCO multi-function transistor tester TC1 Can measure resistors ranging from ohms (Ω) to megaohms (MΩ).
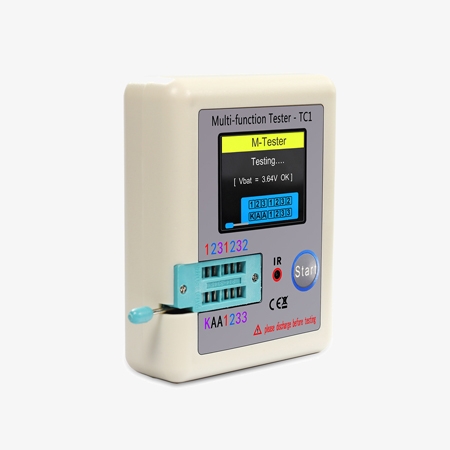

- Dedicated Voltage Regulator Testing: The multifunction transistor meter features independent measurement channels, this hFE transistor tester is specifically designed for testing Zener diodes with a wide measurement range of 0.01-32V, ensuring precision before powering on the components.
- Portable Design: Compact and easy to carry, this MOFEST transistor tester provides convenience and efficiency for on-the-go testing.
- Comprehensive Component Testing: The transistor detector supports real-time testing of capacitors, inductors, resistors, MOSFETs, transistors, and Zener diodes, providing a versatile solution for various electronic components.
- Precise and Reliable Measurements: With specialized features for different components, the digital transistor tester ensures high accuracy and reliability in all measurements.
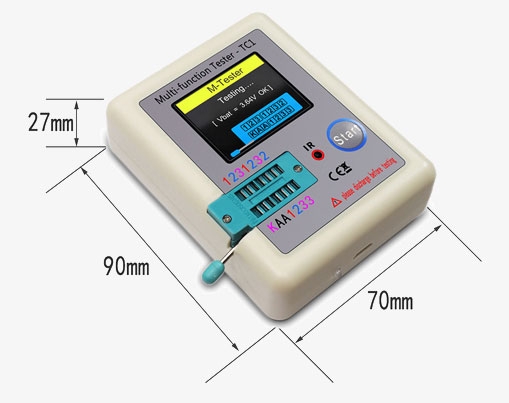
Dimension
Applications
SISCO transistor tester is ideal for product development, household appliance repair, and scientific research, providing precise and efficient testing for a wide range of electronic components. Its versatility makes it suitable for engineers, technicians, and researchers alike.

Appliance Repair
Product Development

Scientific Research

Educational Institutions
| Model | SISCO-TT-TC1 | |
| Component Type | Range | Explanation |
| BJT | / | hFE(DC Current Gain),Ube(Base-Emitter Voltage),Ic(Collector Current), Iceo(Collector Cut-off Current(IB=0)), Ices(Collector short Current), Uf(Forward Voltage of protecting diode) |
| Diode | Forward voltage<4.50V | Forward voltage drop, junction capacitance, reverse leakage current Ir |
| Double Diode | Forward voltage | |
| Zener Diode | 0.01-4.50V(Transistor Test Area) | Forward voltage drop, reverse breakdown voltage |
| 0.01-20V (Zener diode test area) | ||
| MOSFET | JFET | Cg (Gate Capacitance), Id (Drain Current) at Vgs (Gate to Source Threshold Voltage), Uf Forw Voltage of protecting diode) |
| IGBT | Drain current Id under Vgs, protection diode forward voltage drop Uf | |
| MOSFET | Turn-on voltage Vt, gate capacitance Cg, drain resistance Rds, protection diode forward voltage drop Uf | |
| Thyristor | Gate trigger current<6mA | Gate turn-on voltage |
| Capacitor | 25pF-100mF | Capacitance Value, Equivalent Series Resistance ESR, Vloss |
| Resistor | 0.01-50MΩ | Resistance |
| Inductor | 0.01mH-20H | Inductance, DC Resistance |
| Battery | 0.1-4.5V | Voltage value, battery polarity |
Details
Q1: What is transistor tester?
A1: A transistor tester is a device used to test and measure various electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, capacitors, resistors, and more. It helps identify component type, functionality, and key parameters like voltage and resistance.
Q2: How does a transistor tester work?
A2: A transistor tester works by applying a small current to the transistor's terminals to measure its electrical properties. It identifies the type of transistor (NPN or PNP) and checks for key parameters like gain (hFE), leakage current, and junction voltage, helping to determine if the transistor is functioning properly.
Q3: How does the tester identify transistors and diodes?
A3: The tester identifies transistors and diodes by automatically analyzing the connections and properties of the component's terminals. It measures key parameters such as voltage, current, and polarity to determine the type of component and its characteristics.
Tips: Can the transistor tester measure transistor gain (hFE) accurately?
Yes, a transistor tester can measure transistor gain (hFE), but its accuracy depends on the quality of the tester and the testing conditions. Basic testers often provide only an approximate value of hFE, which may vary depending on the operating voltage, current, and temperature during testing. More advanced testers might give more accurate and reliable measurements by applying consistent conditions.
For precision applications, it's recommended to use specialized equipment that can measure hFE under conditions close to the transistor's actual working environment. Even though a basic tester gives a rough estimate, it might not reflect the transistor's real-world performance accurately.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

