High-qulaity handheld nuclear radiation detector is reflected in its robust and durable construction, made with high-resistance materials that ensure optimal performance in any situation. This radiation meter stands out for its advanced functionality, offering audible and visual alarms that alert you to the presence of radioactive contamination.

Backlit LCD Display
- Backlit LCD Display for Any Lighting Condition: The detector features a clear LCD screen with adjustable backlighting, ensuring data is easy to read whether you are indoors, outdoors, in low light, or in bright environments.
- High-Contrast Readout: The backlit display enhances visibility of radiation levels, battery status, and system indicators, making it suitable for night use or dimly lit areas.
- User-Friendly Interface: Large digits and a clean layout on the backlit screen improve readability, reducing eye strain during long measurement sessions.
- Status Indicators at a Glance: The illuminated display clearly highlights alarm notifications, measurement units, and mode selections for fast, accurate interpretation.
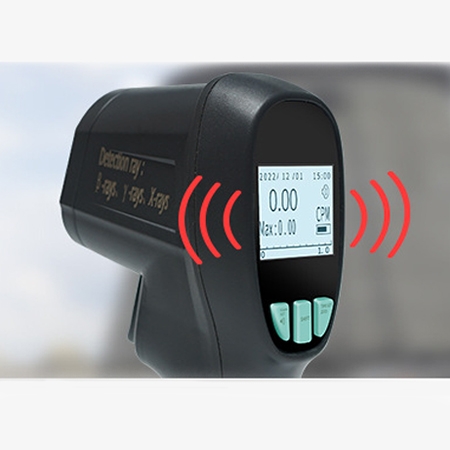

OOver-Limit Alarm Ensures Safety
- Over-Limit Alarm for Enhanced Safety: The detector is equipped with an automatic over-limit alarm that activates when radiation levels exceed the preset threshold, alerting users instantly to potential hazards.
- Audible and Visual Warnings: When unsafe levels are detected, the device triggers both sound and screen indicators, ensuring the user is aware even in noisy or visually restricted environments.
- Customizable Thresholds: Users can set their own alarm limit values based on different work environments, improving adaptability and safety.
- Real-Time Hazard Notification: The fast response of the GM tube ensures the alarm is triggered immediately, helping users take protective action without delay.
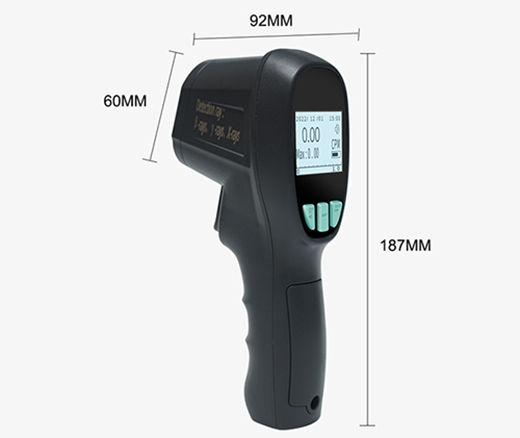
Dimension

Applications
SISCO radiation detector is a device used to detect and measure ionizing radiation, such as alpha, beta, gamma rays, and neutrons. Radiation detectors are used in medical imaging, industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and security to measure ionizing radiation. They help ensure safe radiation levels, detect contamination, and prevent the unauthorized transport of radioactive materials. They’re also crucial in scientific research for studying radiation effects.

Environmental

Security

Industrial
Medical
| Model | SISCO-RD-HZ-550 |
| Sensor Type | Energy-compensated GM tube |
| Measurable Type | β-rays, γ-rays, X-rays |
| Energy Range | 20keV~3.0keV≤±30% (137Cs-) |
| Sensitivity | 80cpm/μSv/(Co-60) |
| Resolution | 0.01μSV/h |
| Measurement Range | 9999μSV/h |
| Real-time Error | ≤3% |
| Power Supply | 5V/USB 3.7V lithium battery/500 mAh |
| Charging Time | 1~2 hours |
| Dimensions | 187*92*60mm |
| Weight | 420g |
Q1: What is a radiation detector?
A1: A radiation detector is a device designed to detect and measure ionizing radiation, such as alpha, beta, gamma rays, and neutrons. These detectors work by sensing the interaction of radiation with matter, often producing an electrical signal that correlates with the intensity or type of radiation present. Radiation detectors come in various types, including Geiger-Müller counters, scintillation detectors, and solid-state detectors, each tailored to detect different forms of radiation or provide varying levels of sensitivity.
Q2: Do radiation detectors need calibration?
A2: Yes, radiation detectors need regular calibration to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Calibration involves adjusting the detector to account for any changes in its performance over time, which can be caused by factors such as aging components, environmental conditions, or variations in detector sensitivity. Regular calibration helps maintain the accuracy of the readings and ensures that the detector provides precise data for assessing radiation levels. Calibration is typically performed using known radiation sources and may be required by regulatory standards to ensure compliance and safety.
Q3: Can radiation detectors detect non-ionizing radiation?
A3: Most radiation detectors are designed to detect ionizing radiation, such as alpha, beta, gamma rays, and neutrons. Non-ionizing radiation, which includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, and visible light, requires different types of sensors. For example:
- Radio frequency (RF) meters and electromagnetic field (EMF) meters are used to measure non-ionizing radiation like radio waves and microwaves.
- Photodetectors (such as photodiodes) measure visible light, while infrared sensors detect infrared radiation.
Tips: How does a Geiger-Müller tube work?
A Geiger-Müller (GM) tube works by detecting ionizing radiation that enters the tube through a thin window or its outer wall. Inside the tube is a low-pressure inert gas and a central anode wire held at high voltage. When radiation passes into the tube, it ionizes the gas molecules, creating free electrons and positive ions. These charged particles trigger a brief electrical discharge between the anode and the tube wall. The detector counts each discharge as a radiation event. These pulses are then converted into readings such as CPM (counts per minute) or µSv/h, allowing the user to monitor radiation intensity.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

