The handheld cable fault detector is designed with "automation and high precision" as its core concept. This cable fault detector incorporates numerous innovative technologies to significantly reduce manual operation and improve fault location efficiency and accuracy.
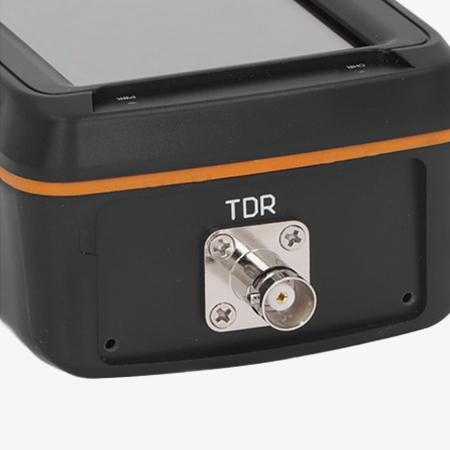

Advanced Signal Processing and High-Speed Computing Architecture
- The DAGC system precisely adjusts gain using digital signals, eliminating waveform distortion at its root. It also supports a pure linear adjustment mode, meeting the sophisticated needs of manual testing professionals while balancing the convenience of automation with the flexibility of manual operation.
- Utilizing an ARM CPU combined with FPGA technology, the cable fault tester boasts high-speed data processing and complex computing capabilities. During testing, the cable fault detector analyzes collected cable signals in real time, quickly comparing fault characteristic parameters and accurately determining the location of the fault waveform, avoiding test delays caused by insufficient computing speed.
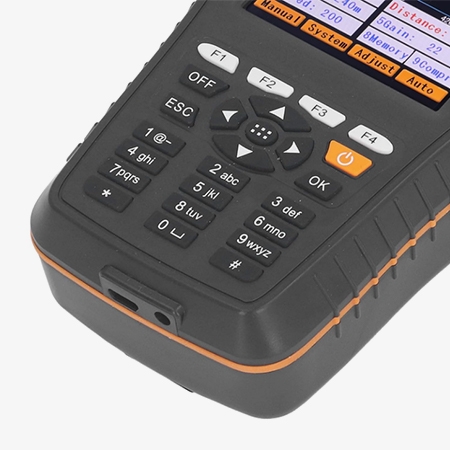

Enhancing the on-site Testing Experience
- The cable fault detector supports direct comparison of test waveforms between faulty and normal lines. Operations and maintenance personnel can view waveform differences between the two lines on a single screen, intuitively identifying the waveform mutation area corresponding to the fault point without repeatedly switching between data points. This significantly reduces troubleshooting time and is particularly suitable for fault location on multi-core cables or complex lines.
- The cable fault indicator features a high-brightness, high-resolution color LCD screen, clearly displaying test waveforms, data parameters, and menu options, even in bright outdoor sunlight, eliminating operational errors caused by blurry screens.
- The portable cable fault locator is lightweight and can be held in one hand or easily stored in a tool bag, making it suitable for mobile applications such as outdoor work at height and underground operations.
Applications
The cable fault locator is suitable for multiple scenarios: troubleshooting high and low voltage cable faults in the power industry, testing communication cables in the communications industry, troubleshooting production cables in industrial enterprises, locating indoor cable problems in the civil construction field, and can also be used for cable fault detection in special environments such as ships, rail transit, mines and oil fields.

Railway

Shopping Mall

Industrial Park

Communications
| Model | SISCO-CFL-HMDL1 | SISCO-CFL-HMDL2 | SISCO-CFL-HMDL4 | SISCO-CFL-HMDL8 |
| Manual Test Maximum Measurement Range | 1KM | 2KM | 4KM | 8KM |
| Intelligent Test Maximum Measurement Range | 4KM | |||
| Maximum Resolution | 0.5M | |||
| Test Blind Zone | OM | |||
| Power Consumption | 1W | |||
| Weight | 0.38KG | |||
| Dimensions | 190mm×84mmx52mm | |||
| Ambient Operating Temperature | -15℃~+45℃ | |||
| Storage Temperature | -20℃~+55℃ | |||
Structure Diagram
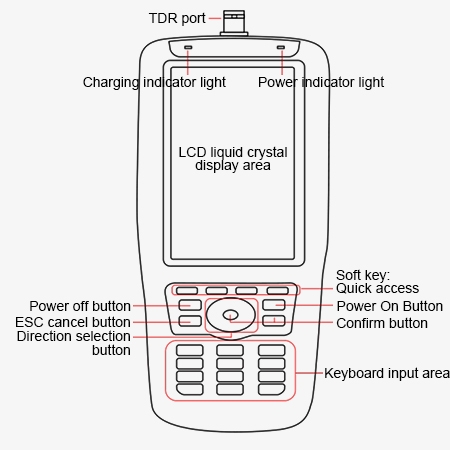
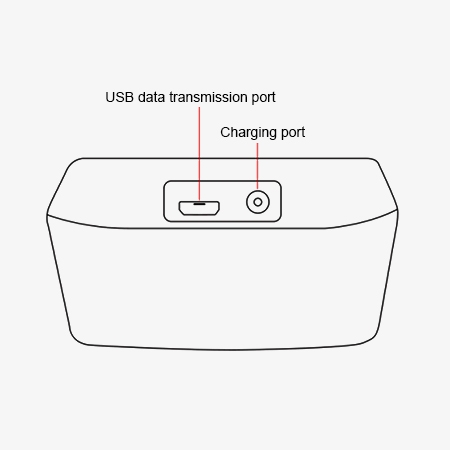
Q1: How to Use a Cable Fault Locator?
A1: To use a cable fault locator, connect the instrument to the faulty cable, select a test mode (such as low-voltage pulse or high-voltage flashover), transmit a signal, analyze the reflected waveform, determine the distance to the fault, and then precisely locate the fault along the cable. After repair, retest to confirm the location.
Q2: How Does a Cable Fault Locator Work?
A2: Cable fault locators typically use technologies such as time domain reflectometry (TDR), bridge technology, and acoustic-magnetic synchronization. They are portable, easy to use, and offer high locating accuracy. They are widely used in cable maintenance and emergency repair in industries such as power, communications, railways, and petrochemicals, significantly improving troubleshooting efficiency and reducing power outage time and repair costs.
Q3: What Factors Affect the Test Accuracy of a Cable Fault Locator?
A3: The test accuracy of a cable fault locator is affected by a variety of factors, including cable length, type, installation environment, and connector quality; the instrument's sampling rate, pulse width, signal processing capabilities, operator experience, external electromagnetic interference, grounding conditions, and fault type (such as low-resistance, high-resistance, flashover, or broken wire). These factors together determine the accuracy and reliability of fault location.
Tips: Common Mistakes When Using a Cable Fault Locator?
Common mistakes when using cable fault locators include not selecting the appropriate test mode for the cable type (e.g., high-voltage power cable, low-voltage control cable), leading to misdiagnosis of faults; not first verifying that both ends of the cable are completely de-energized or unloaded, which can damage equipment or interfere with testing; blindly scanning without first understanding the cable path, which wastes time; and over-reliance on instrument data without considering the cable installation environment (e.g., underground, on a cable tray) and physical inspection (e.g., damaged cable sheath, loose connectors), which can lead to missing the actual fault point.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

