This mechanical oil pressure gauge tester offers multiple ranges and different accuracy levels, featuring anti-vibration and shock resistance, easy installation and sealing, rust prevention, and the ability to isolate special media. It is suitable for harsh environments and various operating conditions, making it highly versatile.
Note: If you need other sizes, please contact customer service.

Ulti-Range, High-Precision, Shock-Resistant
- The mechanical oil pressure gauge tester offers multiple pressure measurement ranges, including 0~16 MPa to 0~160 MPa. Accuracy classes are available in 2.5 and 1.6 grades to meet the accuracy requirements of various operating conditions.
- The pressure reader's gauge head is filled with Recision All Weather Gauge Oil, significantly reducing pointer jitter caused by external vibrations and resulting in more accurate readings.
- The oil-filled pressure gauge features a built-in damping mechanism that effectively "rectifies" pulsating pressure. This instrument can withstand instantaneous pressure shocks, such as sudden pressure relief, maintaining accurate readings even under severe pulsation.

Compatible with Multiple Devices and Special Media
- The pressure test gauge uses a standard API flange for easy installation and sealing, ensuring compatibility with various devices. Equipped with sealing and corrosion-resistant measures, it can operate normally in harsh environments such as outdoor and high-humidity conditions.
- The pressure indicator is designed for special media such as high viscosity and high particle size. The rubber plug inside the instrument can completely isolate the measured medium from the outside of the instrument, preventing the medium from entering the interior and affecting the operation of the components. Therefore, it can be adapted to pressure measurement of special media such as mud, effectively solving the problem of traditional pressure gauges failing due to medium blockage and improving versatility.
Applications
In industrial production, a pressure meter ensures equipment safety and process stability; in public services, a pressure gauge maintains daily operation and safe use; in the medical and health field, a pressure test gauge assists in diagnosis and treatment; in scientific research and high-end manufacturing, a pressure reader supports research and development and reliable equipment operation.

Public Services

Healthcare

High-End Manufacturing

Industrial Production
| Model | SISCO-PG-YK150F | ||
| Nominal Bore Diameter | 2-1/16in | ||
| Flange Pressure | 10000psi | ||
| Outer Diameter (OD) | 200mm | ||
| Thickness (T) | 44.1mm | ||
| Threaded Hole (BD) | 23mm | ||
| Threaded Hole Distribution (BC) | 158.8mm | ||
| Weight | 16kg | ||
| Operating Ambient Temperature | -40℃~55℃ | ||
| Measuring Range (MPa) | 0~16, 0~25 | Accuracy level | 2.5 |
| 0~40, 0~60, 0~80, 0~100, 0~120, 0~160 | 1.6 | ||
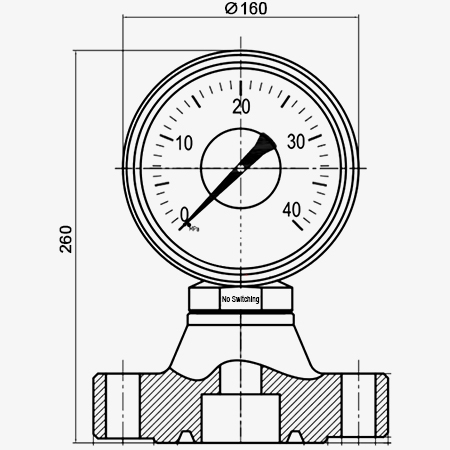
Structural diagram

Q1: How does a tire pressure gauge work?
A1: A tire pressure gauge works by measuring the air pressure inside a tire. When you press the gauge onto the tire's valve stem, air from the tire enters the gauge. Inside the gauge, a calibrated spring or sensor measures the force exerted by the air pressure. This force is then translated into a readable value on the gauge's dial or digital display, indicating the tire's pressure in units such as PSI (pounds per square inch) or kPa (kilopascals).
There are different types of tire pressure gauges, including analog (dial) gauges, digital gauges, and stick gauges. Analog tire pressure gauges use a mechanical spring to provide a pressure reading, while digital tire pressure gauges use electronic sensors to measure the pressure and display the result on a screen. Stick gauges, also known as pencil gauges, have a simple, retractable rod that is pushed out by the air pressure, showing the reading on a marked scale. All these gauges serve the same purpose: ensuring that your tires are inflated to the correct pressure for optimal performance and safety.
Q2: Which type of tire pressure gauge is most accurate?
A2: The most accurate type of tire pressure gauge is generally considered to be the digital gauge. Here are a few reasons why:
- Precision and Readability: Digital gauges typically provide precise readings, often to a decimal point, which can be easier to read compared to analog gauges. They eliminate the parallax error that can occur when reading a dial gauge.
- Consistency: Digital gauges are less likely to be affected by environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can sometimes impact the accuracy of mechanical (analog) gauges.
- Calibration: Digital gauges often maintain their calibration longer than analog gauges. However, it's still important to occasionally check and recalibrate any tire pressure gauge to ensure its accuracy.
Q3: Is a tire inflator the same as an air compressor?
A3: A tire inflator and an air compressor are not the same, although they serve related purposes. A tire inflator is specifically designed to inflate tires and usually comes with built-in pressure gauges and attachments that fit onto tire valves. It is typically portable, easy to use, and can be powered by a car's cigarette lighter or battery.
An air compressor, on the other hand, is a more versatile tool that can be used for a variety of tasks beyond inflating tires, such as powering pneumatic tools, painting, and cleaning. Air compressors are generally larger and more powerful than tire inflators, often requiring a separate power source. While an air compressor can be used to inflate tires with the appropriate attachments, its primary function is to provide compressed air for a wider range of applications.
Tips: How to understand a pressure gauge?
The line of sight should be perpendicular to the dial to avoid parallax caused by viewing angle deviation. First, identify the pressure unit marked on the dial (e.g., MPa, kPa, PSI), then read the main scale value indicated by the pointer, estimating to one decimal place of the smallest scale division. For multi-pressure gauges with range selection, be sure to identify the currently used range first. If the pointer fluctuates slightly, take the average value or the middle position as the reading. After reading, record the value and indicate the unit to ensure the accuracy and validity of the data, providing a reliable basis for subsequent analysis or fault diagnosis.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

