SISCO J-type thermocouple offers versatile and cost-effective temperature monitoring solutions for chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, and food processing industries. Its reliable performance ensures accurate temperature control across a wide range of industrial applications, making it an essential tool in demanding environments.

Wide Temperature Range for Industrial Use
- SISCO J-type thermocouple provides reliable measurement up to approximately 750°C, making it suitable for many industrial temperature monitoring applications.
- It offers good measurement accuracy and stability in mid-range temperatures, especially in reducing or vacuum environments.
- J-type thermocouple is commonly used in older controllers, PLCs, and heat-treating equipment, ensuring broad system compatibility.
- Its iron–constantan design performs well in ovens, furnaces, plastic extrusion machines, and other equipment that does not require high-temperature oxidation resistance.
Applications
SISCO J-type thermocouple is widely used in applications such as industrial furnaces, heat-treating equipment, ovens, and kilns, especially where reducing or vacuum environments are present. It is also common in plastic extrusion and injection molding machines, as well as food processing and HVAC systems that operate within its moderate temperature range.

Industrial Furnaces

Ovens

Kilns

Heat-Treating Equipment
Thermocouple Temperature Range Chart
| Category | Type of sensing element | Relationship between wire diameter and temperature | ||
| Thermo wire diameter (mm) | Long-term temperature (℃) | Short-tem temperature (℃) | ||
| Platinum Rhodium 30 - Platinum Rhodium 6 | B type | Φ0.5 | 1600 | 1800 |
| Platinum Rhodium 13 - Platinum | R type | Φ0.5 | 1300 | 1600 |
| Platinum Rhodium 10 - Platinum | S type | Φ0.5 | 1300 | 1600 |
| Nickel chromium silicon - Nickel silicon magnesium | N type | Φ0.3 | 700 | 800 |
| Φ0.5 | 800 | 900 | ||
| Φ0.8, Φ1.0 | 900 | 1000 | ||
| Φ1.2, Φ1.6 | 1000 | 1100 | ||
| Φ2.0, Φ2.5 | 1100 | 1200 | ||
| Φ3.2 | 1200 | 1300 | ||
| Nickel chromium - Nickel silicon | K type | Φ0.3 | 700 | 800 |
| Φ0.5 | 800 | 900 | ||
| Φ0.8, Φ1.0 | 900 | 1000 | ||
| Φ1.2, Φ1.6 | 1000 | 1100 | ||
| Φ2.0, Φ2.5 | 1100 | 1200 | ||
| Φ3.2 | 1200 | 1300 | ||
| Nickel chromium - Copper nickel | E type | Φ0.3 | 350 | 450 |
| Φ0.5 | 450 | 550 | ||
| Φ0.8, Φ1.0 | 550 | 650 | ||
| Φ1.2, Φ1.6 | 650 | 750 | ||
| Φ2.0, Φ2.5 | 750 | 900 | ||
| Iron - Constantan | J type | Φ0.3, Φ0.5 | 300 | 400 |
| Φ0.8, Φ1.0 | 400 | 500 | ||
| Φ1.2, Φ1.6 | 500 | 600 | ||
| Φ2.0, Φ2.5 | 600 | 750 | ||
| Copper - Copper nickel | T type | Φ0.2 | 150 | 200 |
| Φ0.3, Φ0.5 | 200 | 250 | ||
| Φ1.0 | 250 | 300 | ||
| Φ1.6 | 350 | 400 | ||
Thermowell Application Temperature Range Chart
| Thermowell material | Long-term temperature | Short-term temperature |
| Corundum CT1 | 1600 | 1800 |
| High alumina CT2 | 1300 | 1600 |
| Nickel base wrought superalloys 3YC52 | 1300 | 1350 |
| Nickel base wrought superalloys GH3039 | 1250 | 1320 |
| Nickel base superalloys GH3030 | 1200 | 1250 |
| Heat resistant stainless steel 2Cr25Ni20 | 1200 | 1250 |
| Silicon carbide | 1100 | 1150 |
| Stainless steel 316L | 900 | 950 |
| Stainless steel 1Cr18Ni9Ti | 800 | 900 |
Thermowell Installing Form (unit: mm)
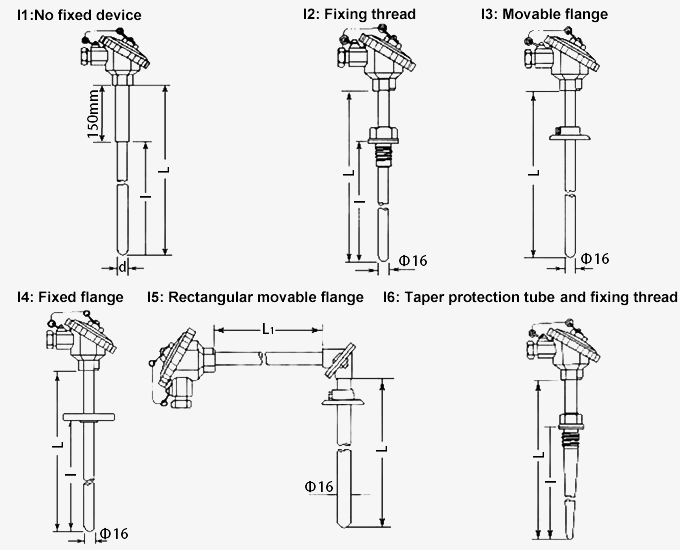
Selection Chart
| Total length of thermowell (L or L*L1) | Branch number | Thermowell installing form | Protection head form | Diameter and material of thermowell |
| 300~2150mm (for I1, I2, I3, I4); 500*500mm, 750*500mm, 750*750mm (for I5); 225~450mm (for I6) |
B1: Single branch; B2: Double branch |
I0: No thermowell; I1: No fixed device; I2: Fixing thread; I3: Movable flange; I4: Fixed flange; I5: Rectangular movable flange; I6: Taper thermowell and fixing thread |
C1: No protection head; C2: All stainless steel protection head; C3: Waterproof protection head; C4: Explosion-proof protection head |
D0: Φ16mm; D1: Φ25mm, double-deck; D2: Φ16mm high quality aluminum; D3: Φ20mm high quality aluminum |
Thermocouple Assembly Installation Diagram
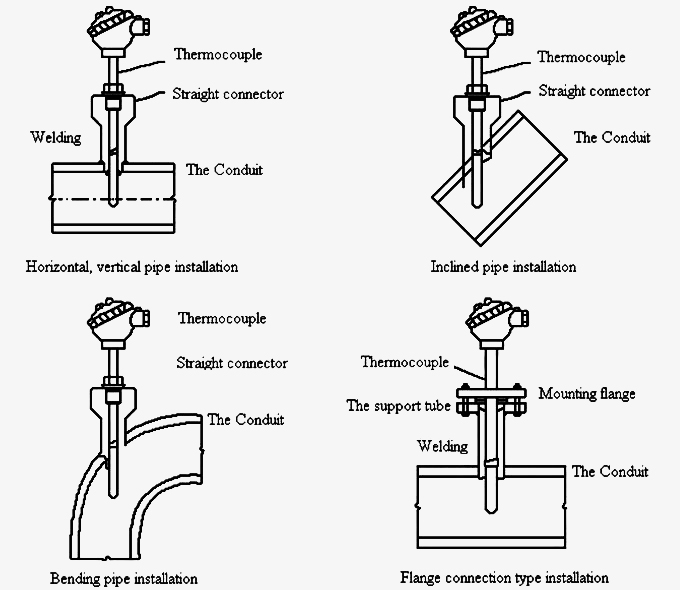
| Design serial number | 1 | |||||
| Structure diagram | 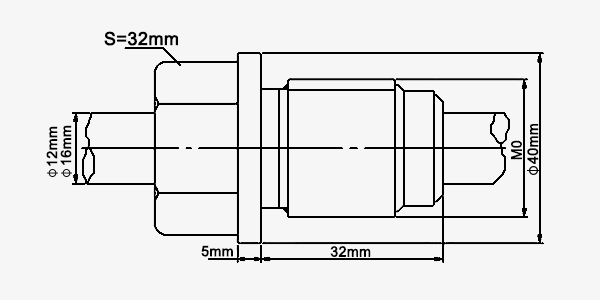 |
|||||
| Name | Fixed thread | |||||
| Size | M27*2 (default), G3/4", M33*2, G1", other | |||||
| Protection tube | Diameter | φ12mm, φ16mm, other | ||||
| Texture of material | 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 2Cr25Ni20, other | |||||
| Withstand voltage | ≤10MPa | |||||
| Design serial number | 2 | |||||
| Structure diagram | 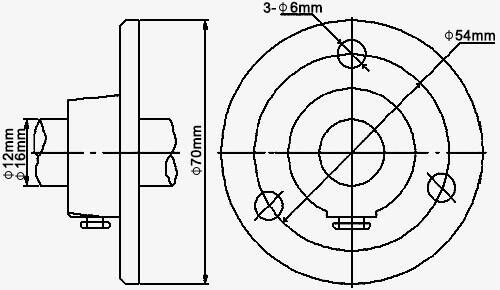 |
|||||
| Name | Movable flange | |||||
| Protection tube | Diameter | φ12mm, φ16mm, other | ||||
| Texture of material | 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 2Cr25Ni20, other | |||||
| Withstand voltage | Atmospheric pressure | |||||
| Design serial number | 3 | |||||
| Structure diagram | 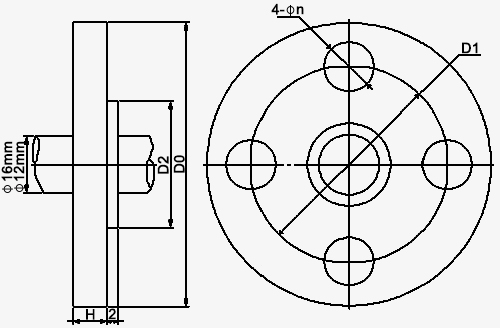 |
|||||
| Name | Fixed flange | |||||
| Size | DN15mm (default) | D0 | 95mm | DN20mm | 105mm | |
| D1 | 65mm | 75mm | ||||
| D2 | 45mm | 55mm | ||||
| φn | 4-φ14mm | 4-φ14mm | ||||
| DN25mm | D0 | 115mm | DN32mm | 140mm | ||
| D1 | 85mm | 100mm | ||||
| D2 | 65mm | 78mm | ||||
| φn | 4-φ14mm | 4-φ18mm | ||||
| DN40mm | D0 | 150mm | DN50mm | 165mm | ||
| D1 | 110mm | 125mm | ||||
| D2 | 85mm | 100mm | ||||
| φn | 4-φ18mm | 4-φ18mm | ||||
| H | 12mm | |||||
| Protection tube | Diameter | φ12mm, φ16mm, other | ||||
| Texture of material | 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 2Cr25Ni20, other | |||||
| Withstand voltage | ≤6.4MPa | |||||
| Design serial number | 4 | |||||
| Structure diagram | 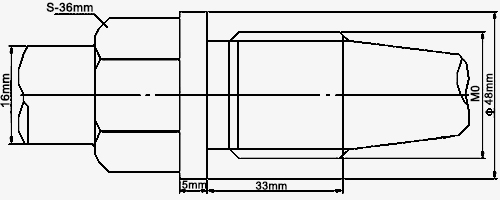 |
|||||
| Name | Conical fixed thread | |||||
| Size | M27*2 (default), M33*2, G1", other | |||||
| Protection tube | Diameter | φ12mm, φ16mm, other | ||||
| Texture of material | 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 2Cr25Ni20, other | |||||
| Withstand voltage | ≥30MPa | |||||
Q1: What is a thermocouple?
A1: A thermocouple is a commonly used temperature-measuring component in a temperature-measuring instrument. It directly measures the temperature and converts the temperature signal into a term electromotive force signal, which is converted into the temperature of the measured medium by an electric meter (secondary meter). The shape of various thermocouples is often very different due to the needs, but their basic structure is almost the same, usually composed of the hot electrode, insulating sleeve protection tube and junction box, etc., usually with a display instrument, recording instrument and electronic adjustment Used in conjunction with the device.
Q2: What is a K-type thermocouple used for?
A2: As a transmitter for measuring temperature, industrial K-type thermocouples are usually used in conjunction with display instruments, recording instruments and electronic regulators. It can directly measure the surface temperature of liquid, vapor and gaseous media and solids ranging from 0°C to 1000°C in various production processes.
Q3: How does a thermocouple work?
A3: A thermocouple is the connection of two different conductors or semiconductors into a closed circuit. When the temperature of the two junctions is different, an electromotive force will be generated in the circuit. This phenomenon is called the hot spot effect, also known as the Seebeck effect. The end directly used to measure the temperature is called the working end, and the other end is called the cold end. The cold end is directly connected to the instrumentation or supporting equipment, and the display instrument will point out the electromotive force generated by the thermocouple.
Tips: What are the common types of thermocouples?
Common thermocouple types include K, J, T, E, N, and the high-temperature platinum–rhodium types R, S, and B. Type K is the most widely used because of its broad temperature range and good durability. Type J is common in older equipment and works well in reducing environments. Type T is highly accurate at low temperatures, while Type E provides a strong signal output.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

