The high-pressure pH glass electrode can be customized for various working environments and comes equipped with an integrated temperature sensor, enabling automatic temperature compensation. It delivers precise measurement results with a fast and stable response.
High anti-interference and good stability
- Malleable ring-type PTFE protection diaphragm can prevent measurement media deposition and blockage.
- The shell material is high-tenacity glass, high temperature resistant, high pressure resistant.
- Solid reserve salt ring design for low ion concentration or high flow rate environment.
- PH electrode adopts a Germany Cartridge-style conducting system, free of silver ions, with better stability.
- PC protection cover can store saturated KCL solution to keep the electrode active.
- Accessories: PTFE sheath or stainless steel sheath. Increase the acid and alkali resistance of the electrode, easy to install.
- High-quality low-noise cable can achieve 60m long-distance signal transmission.
Application
pH Electrode is widely used in the continuous testing and monitoring of pH, ORP, and temperature in thermal power, chemical fertilizer, metallurgy, environmental protection, pharmaceutical, biochemical, food, drinking water, etc.

| Model | SISCO-CPH5806 |
| Weight | 1kg |
| Measuring range | 0-14pH |
| Temperature range | -5℃-130℃ |
| Thermistor | Pt1000 |
| Compressive strength | 0.6MPa |
| Installation size | PG13.5 pipe thread |
| Shell material | Glass |
| Connection | Low noise cable directly led out/VP6 |
| Cable length | Standard configuration 120mm (Customizable on demand) |
| Cable | Can be equipped with VP cable |
Installation
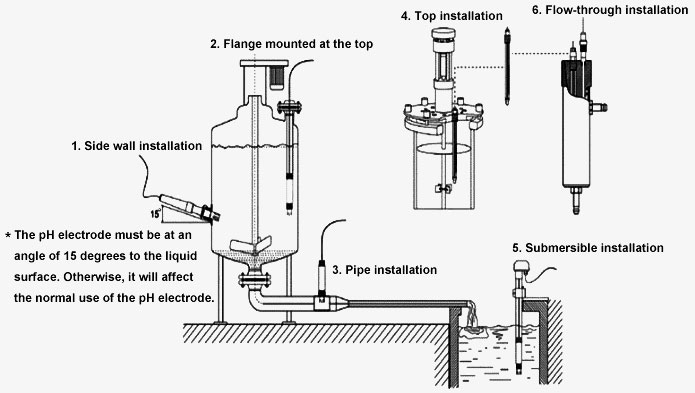
- Side wall installation (*The pH electrode must be at an angle of 15 degrees to the liquid surface. Otherwise, it will affect the normal use of the pH electrode.)
- The flange mounted at the top
- Pipe installation
- Top installation
- Submersible installation
- Flow-through installation
Q1: What is a pH electrode?
A1: The pH electrode is also called the pH probe pH sensor. The pH electrode is the part of the pH meter that is in contact with the substance to be measured and is used to measure the electrode potential.
Q2: Why do pH electrodes need to be soaked?
A2: The pH electrode must be soaked before use, because the pH bulb is a special glass membrane with a thin hydrated gel layer on the surface of the glass
membrane, which can only interact with the H+ ions in the solution under fully wet conditions. the response to. At the same time, after soaking the glass
electrode, the asymmetric potential can be greatly reduced and tend to be stable.
Q3: What is a reference electrode?
A3: An electrode with a known and constant electrode potential that does not respond to the activity of hydrogen ions in solution is called the reference electrode. Reference electrodes include mercurous sulfate electrodes, calomel electrodes, and silver/silver chloride electrodes. The most commonly used are calomel electrodes and silver/silver chloride electrodes. The role of the reference electrode in the measurement cell is to provide and maintain a fixed reference potential, so the requirements for the reference electrode are that the potential is stable and reproducible, the temperature coefficient is small, and the polarization potential is small when current flows.
Tips: How to clean the electrode?
- Metal ions attached the measuring end of the electrode into 0.5 mol/I hydrochloric acid solution for 5 minutes, shake the electrode several times quickly (stirring) before taking it out, rinse with deionized water after taking it out, and soak in 3.0 mol/I potassium chloride solution for 4 hours.
- Contamination by organic matter
Dip the measuring end of the electrode into anhydrous ethanol (or solvent capable of dissolving the organic material) for 15 minutes, shake the electrode rapidly (stirring) before removing, rinse with deionized water and soak in 3.0 mol/I potassium chloride solution for 4 hours. Note: The electrode shell material is polycarbonate, the organic sample or cleaning solution may corrode the electrode shell. - 3. Inorganic cleaning
Dip the measuring end of the electrode in 0.1mol/I EDTA solution or 0.1mol/l hydrochloric acid solution for 15 minutes, shake the electrode several times (stirring) quickly before taking out, rinse with deionized water after taking it out, and soak in 3.0mol/I potassium chloride solution for 4 hours. - 4. Protein precipitation
Soak the measuring end of the electrode in 1% hydrochloric acid solution of pepsin (concentration of hydrochloric acid is 0.1 mol/I) for 15 minutes, shake the electrode rapidly several times (stirring) before removing, rinse with deionized water after removing, soak in 3.0 mol/I potassium chloride solution for 4 hours. - 5. Grease adhesion
Immerse the measuring end of the electrode in a weak alkaline detergent for 15 minutes. After removal, rinse with deionized water and immerse in 3.0 mol/I potassium chloride solution for 4 hours. - 6. Regeneration of the glass-sensitive film
Soak the measuring end of the electrode in 4% hydrofluoric acid solution for 3-5 seconds, then rinse with 1:1 hydrochloric acid solution for 10 seconds. The hydrochloric acid solution was rinsed for 10 seconds, cleaned with distilled water, and stored in a 3.0 mol/I potassium chloride solution soaked for 24 hours.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

