Infrared thermometer is an instrument that uses infrared radiation energy to measure the temperature of an object. It is mainly composed of an optical system, a detector, a signal processing circuit and a display device. The working principle of an infrared thermometer is mainly based on the thermal radiation characteristics of an object and the relationship between thermal radiation energy and temperature. In this page, SISCO will introduce the working principle of infrared thermometer briefly to help you have a better understanding of it.
First, the infrared thermometer focuses the infrared radiation emitted by the object onto the detector through an optical system. The higher the temperature of the object, the greater the infrared radiation energy emitted. The infrared radiation energy received by the detector will change accordingly with the change of the object's temperature.
Secondly, the detector converts the received infrared radiation energy into an electrical signal, and amplifies, filters and linearizes it through the signal processing circuit, and finally converts it into a voltage signal that is proportional to the object's temperature.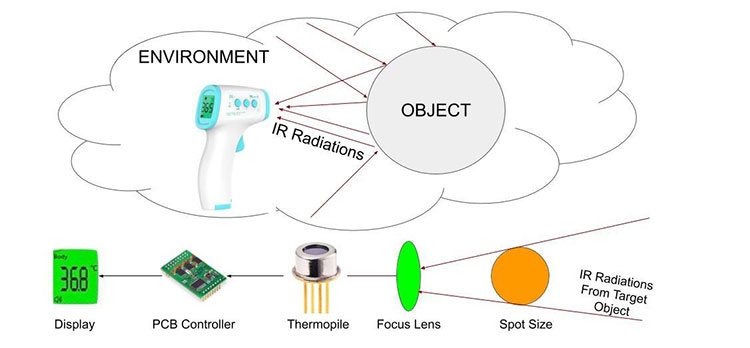
Then, the voltage signal processed by the signal processing circuit will be sent to the display device, and the temperature value of the object will be displayed through the display device. In some advanced infrared thermometers, the temperature can also be recorded, stored and analyzed.
In general, the working principle of an infrared laser thermometer is to utilize the relationship between the infrared radiation energy emitted by an object and its temperature, and through the synergistic effect of optical systems, detectors, signal processing circuits, and display devices, to achieve rapid and accurate measurement of the object's temperature.
The working principle of infrared thermometer is simple and easy to understand, but in practical application, we need to pay attention to some factors that affect the measurement accuracy. For example, the absorption and scattering of infrared radiation by ambient temperature, humidity, gas and dust will affect the temperature measurement accuracy. Therefore, when using infrared thermometer, it is necessary to perform reasonable calibration and compensation according to the actual situation to ensure the accuracy of the measurement results.
In addition, in practical applications, infrared temperature gauges also need to consider factors such as measurement distance, measurement angle, and emissivity of the target surface. Different infrared thermometers have different measurement distance ranges and measurement angle ranges, which need to be selected according to actual measurement requirements.
In a word, the working principle of infrared thermometer is based on the thermal radiation characteristics of objects and the relationship between thermal radiation energy and temperature. Through the synergy of optical system, detector, signal processing circuit and display device, it can achieve fast and accurate measurement of object temperature. In practical applications, it is necessary to consider various factors that affect the measurement accuracy, and perform reasonable calibration and compensation to ensure the accuracy of the measurement results. If you would like to purchase an infrared thermometer or other test and measurement device, you can visit our sisco online store.

