The linear variable differential transformer is a precision measuring tool characterized by high accuracy, high reliability, and ease of use, particularly suitable for critical applications such as quality control, online inspection, and precision measurement.
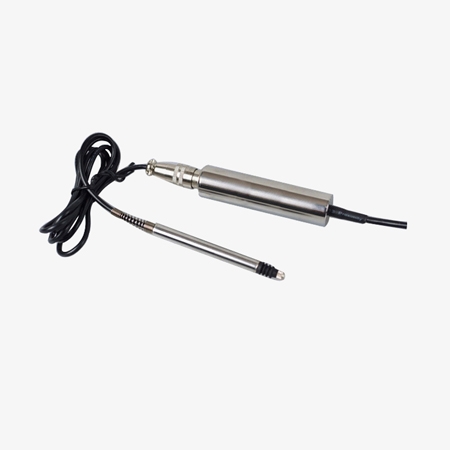

Flexible Power Supply, Adaptable to Multiple Outputs
- The LVDT displacement transducer offers multiple measurement range options, including 2mm, 5mm, 8mm, and 10mm, to meet the needs of different application scenarios.
- With a resolution of 1μm and excellent repeatability, its slip-point-free design not only avoids accuracy degradation caused by mechanical wear but also significantly extends its service life.
- It offers flexible power supply options, supporting AC signal power and an external transmitter with a wide voltage input range of 9-28VDC (recommended voltage varies depending on the output type: 12VDC for 0-5V output, 15VDC for 0-10V output, and 24VDC for current output).
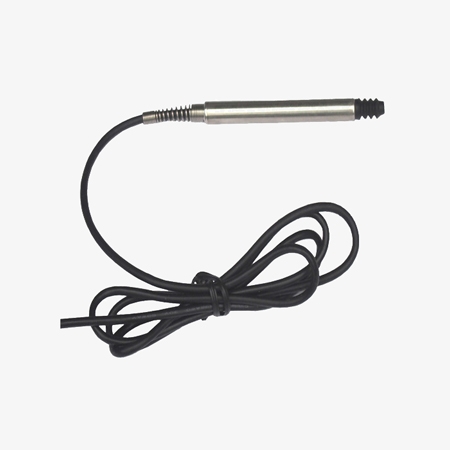

Multiple Signal Outputs for Direct Connections
- The linear variable displacement transducer offers a variety of output types, including 0-5V and 0-10V standard voltage signals, 4-20mA standard current signals, and RS-485 digital signals. It can directly interface with industrial control systems such as computers and PLCs without the need for additional signal conversion equipment.
- The sensor body features a pencil-shaped structure with an outer diameter of 8mm, making it compact and easy to install in confined spaces. The probe is made of high-hardness, wear-resistant zirconia material, and the moving part of the probe axis is equipped with precision guide rails, improving structural stability and wear resistance.
- The electronic circuitry is sealed within a 304 stainless steel tube, providing excellent protection and allowing it to operate stably in harsh industrial environments such as humid and dusty conditions without requiring additional protective measures.
Applications
Displacement sensors are indispensable in four core areas: first, industrial automation, used for precise positioning and control of robots and production lines; second, precision detection and measurement, ensuring workpiece dimensions and processing quality; third, scientific research, supporting precision experiments in materials and micro-nano fields; and finally, equipment health and safety monitoring, monitoring the deformation and vibration of key structures in real time to prevent failures.

Precision Testing

Scientific Research
Equipment Safety

Industrial Automation
| Model | SISCO-DS-SOPH8 |
| Excitation Voltage | 3Vrms (1~3Vrms) |
| Excitation Frequency | 5KHz (1~10KHz) |
| Displacement Range | 2mm, 5mm, 8mm, 10mm |
| Output Signal | AC signal or transmitter output 0~5V (9~28V DC power supply) |
| AC signal or transmitter output 0~10V (15~28V DC power supply) | |
| AC signal or transmitter output 4~20mA (two-wire, 15~28V DC power supply) | |
| AC signal or transmitter output digital RS485 (9~12V DC power supply) | |
| Linearity Error | Analog output: ±0.25%, Digital output: 0.25%, 0.1%, etc. selectable |
| Repetition Error | 1μm |
| Resolution | ≤0.1μm (maximum), digital output is 16-bit |
| Operating Temperature | -25℃ ~+85℃ |
| Temperature Coefficient | Zero point ≤0.01%F.S/℃ |
| Sensitivity ≤0.025%F.S/℃ |
Q1: What Is Linear Displacement?
A1: Linear displacement refers to the change in position of an object along a straight line, and its movement is usually quantified by measuring the distance from the starting point to the ending point. In industrial applications, accurate measurement of linear displacement is crucial for controlling mechanical motion, positioning, and monitoring.
Q2: How to Reduce Measurement Noise in Displacement Sensors?
A2: To reduce measurement noise, ensure that the steel cable is installed horizontally (deviation ≤ ±3°), keep the pulleys clean, and avoid dust accumulation; install protective devices in harsh environments, and connect the circuit correctly (e.g., connect the load before powering on) to reduce mechanical and electromagnetic interference.
Q3: How to Maintain a Displacement Sensor for Long-Term Accuracy?
A3: To maintain the long-term accuracy of general displacement sensors: ensure stress-free installation and avoid exceeding the range or harsh environments; regularly clean the probe and contact surface, check for wear on mechanical parts, and calibrate data on time.
Tips: How Far Should a Displacement Sensor Be Placed From the Target?
The distance between a displacement sensor and the target is not a fixed value, but depends entirely on its type and range. For contact sensors (such as LVDTs), the probe needs to be in physical contact with the target to measure the relative displacement relative to its zero point. For non-contact sensors (such as laser, ultrasonic, and eddy current sensors), they must be placed at their optimal working distance, which is usually specified by the manufacturer. Placing the sensor within its designed linear measurement area will cause signal saturation, a sharp drop in accuracy, or even complete failure to measure if the sensor is too close or too far away.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

