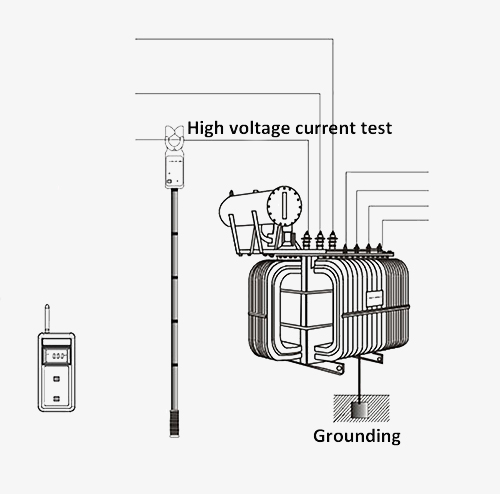
The wireless clamp meter measures AC current to 1200 amp, and the jaw size is Φ48mm. The wireless clamp current meter can replace the high and low voltage transformation ratio tester, that is, measure the high and low voltage currents of the primary circuit and the secondary circuit respectively, and then calculate the high and low voltage transformation ratio. The insulation rod is light and has the characteristics of moisture resistance, high-temperature resistance, impact resistance, bending resistance, and high insulation.
Wireless transmission, clearer data
- The transformer and receiver adopt 30-meter wireless transmission
- View test data in real-time, easy to use

Clamp closure for higher resolution
- CT design, closed mutual inductance
- Using resolution up to 0.01mA
Features
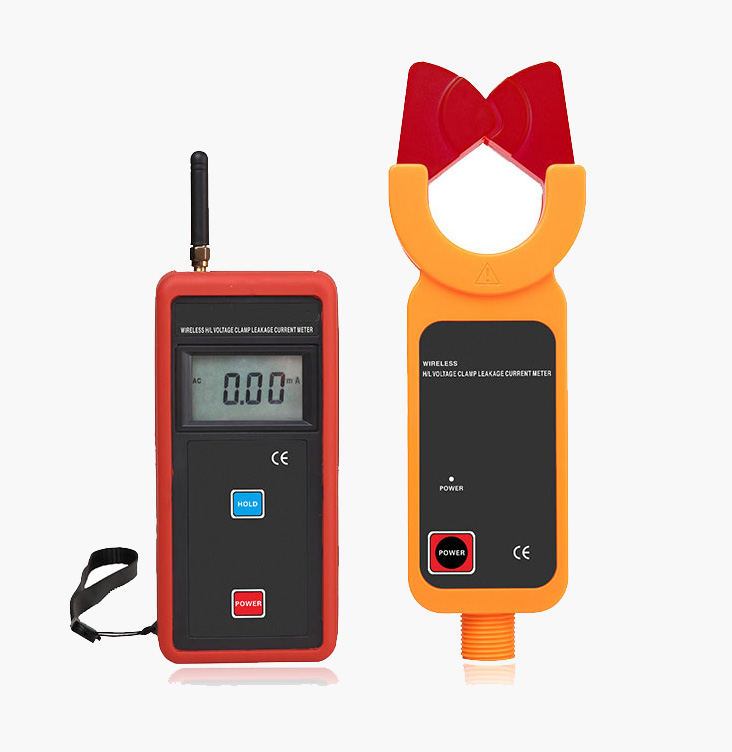

Wireless AC clamp meter with 0.00mA-600A AC high current range, 1mA resolution, and φ48mm CT size.
- The current clamp adopts magnetic shield and CT digital integration technology, with strong anti-interference, high accuracy, and stable test.
- The innovative automatic plug and pull structure makes the meter easy to clamp or withdraw the tested wire by pressing or pulling the insulation rod, saving time and convenience.
- Peak hold, data hold, and data memory function.
Applications
sisco clamp current meter is available with a measuring range of 0mA-60A AC/DC. The clamp ammeter is especially suitable for places with dense wiring (power metering systems, high-speed rail systems, automotive circuit maintenance, etc.), and non-contact current measurements to ensure safe operation. The instrument is small in size, high in precision, stable in performance and perfect in function, and is one of the necessary tools for electrical safety inspection and maintenance.

| Model | SISCO-ETCR9000B |
| Current Range | 0.00mA-1200A |
| Resolution | 1mA |
| Accuracy | 0mA-99.9A: ±1%rdg±5dgt 100A-599: ±1.5%rdg±5dgt 600A-1200A: ±2%rdg±5dgt |
| CT Size | φ48mm |
| Meter Dimensions | 76mm×255mm×31mm Receiver: 78mm×165mm×42mm |
| Weight | 3630g |
| Power Supply | 6V DC (LR03×4pcs alkaline dry batteries) |
| LCD Size | 47mm*28.5mm |
| Sampling Rate | 2 times/second |
| Communication Interface | Wireless transmission, straight distance of 30m |
| Data Storage | 99 groups, stored process display MEM symbol, "FULL" symbol display indicate that storage full |
| Peak Hold | Automatically hold the highest test value |
| Data Hold | In usual test mode, press the HOLD key to keep data, "HOLD" symbol display |
| Overflow Display | Exceed measure range overflow function: "OL A" symbol display |
| Polarity Indication | In DC current test auto-identified and display the "-" symbol |
| Auto Shut Down | 15 minutes after boot up, the meter shuts down automatically without any operation, to reduce battery consumption |
| Battery Voltage | Battery voltage lower than 7.2V will display a low battery voltage symbol, and remind to replace the battery |
| Working Current | 5mA |
| Line Voltage | Below 110kV current test, operate with insulation rods |
| Insulation Rod Dimension | Ф32mm 1m×5 piece |
| Insulation Rod Withstand Voltage | 110kV ( 5PCS insulation rod connection) |
| Accessories | Meter: 1PCS; Receiver: 1PCS; Insulation rod (1m): 5PCS; Tool bag: 1SET |
Q1: What is clamp ampere meter?
A1: A clamp ammeter is a combination of a current transformer and an ammeter. The iron core of the current transformer can be opened when the wrench is tightened; the wire through which the measured current passes can pass through the gap opened by the iron core without being cut off, and the iron core is closed when the wrench is released.
Q2: How does a current clamp meter work?
A2: A clamp meter is a clothespin-shaped instrument that can be clamped around a live wire in order to measure the current it's carrying. As a measurement principle, clamp meters detect the magnetic field emitted by current flowing in a wire in order to measure the current value.
Q3: How to use a clamp ammeter?
A3: When using a clamp ammeter to detect the current, be sure to clamp a measured wire (wire). If two (parallel wires) are clamped, the current cannot be detected. In addition, when the center (core) of the clamp ammeter is used for detection, the detection error is small. When checking the power consumption of home appliances, it is more convenient to use a line splitter. Some line splitters can amplify the detection current by 10 times, so the current below 1A can be amplified before detection. Use a DC clamp ammeter to detect the DC current (DCA), if the current flows in the opposite direction, it will display a negative number. This function can be used to detect whether the car's battery is in a charging state or a discharging state.
Tips: How does a clamp meter read?
- Select gear and range. Turn the meter switch to the DC current "mA" position, and select the correct range according to the measured current. If the current is not known, in order to prevent the current from being too large and exceeding the range, you can first place the DC current at the highest gear for testing. If the range is too large, then reduce the range until the range is appropriate.
- Connect the circuit in series. When the multimeter measures current, the test leads must be connected to the current in series, and the red test lead is connected to the high potential end of the circuit, and the black test lead is connected to the low potential end of the current.
- Reading method: 1. Correctly select the scale line for reading. 2. Converted current value: Current value = the number of scales pointed by the pointer × the size of the range / the maximum value of the selected scale.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

